Docker containers are a great way to build, design, and deploy applications. Docker provides tons of free Docker images available on the Docker Hub registry such as Ubuntu, CentOS, MySQL, etc. This makes it very easy for users to directly pull an image from Dockerhub, create containers associated with them, and immediately start working on them.
Another way to use them is by pulling them using FROM instruction inside a Dockerfile and building new image layers on top of it to customize the image. A very important official image provided by Dockerhub is the Nginx image.
Nginx is a popular Web Server that is widely used all over the world. It is fast, reliable, stable, static, and is used by tons of programmers and application developers as a reverse proxy that sits before their APIs. It is free and open-source and can be run on a variety of operating systems.
In this guide, we will look at three different ways through which we can create and deploy an Nginx Web Server inside a Docker container and access it on our local host machine. We will first use the Docker run command to directly pull and run a container associated with the Nginx image. We will then look at how to deploy static web applications using the Nginx Web Server inside Docker and access these applications on our browser on a local machine.
Finally, we will achieve the same thing using a Dockerfile. So, without any further delays, let’s get started. Please note that you would need access to a Linux machine with Docker installed in it, sudo privileges, and a Dockerhub account logged in through the command line.
Method 1: Using the Docker Run Command
We know that the Docker run command can be used to run containers associated with any Docker image. Even if we don’t have the image in our local machine, it will pull an existing image directly from the Dockerhub registry and create a container associated with it. Let’s see the general syntax of the Docker run command first.
$ docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARGUMENTS...]
In the above command, we can use options such as -i (interactive) to run the Docker container in interactive mode and input commands to its bash, -t (pseudo-TTY), --rm (to automatically remove containers after exit), --name (to provide names to the container), -p (to publish ports), etc. Let’s see the command to create and run an Nginx container directly.
$ docker run -it --rm -d -p 8080:80 --name=webserver nginx
Here, we have used the -i and -t options to run the container interactively, the --rm option to delete the container on exit, -d option to run the container in the background or detached mode, and the --name option to provide a name to the container.
Finally, we have provided the name of the Docker image that we want to pull. We have also used the -p option to publish port 8080 of the container to port 80 of the host machine.
Let’s try to execute this command inside the terminal.
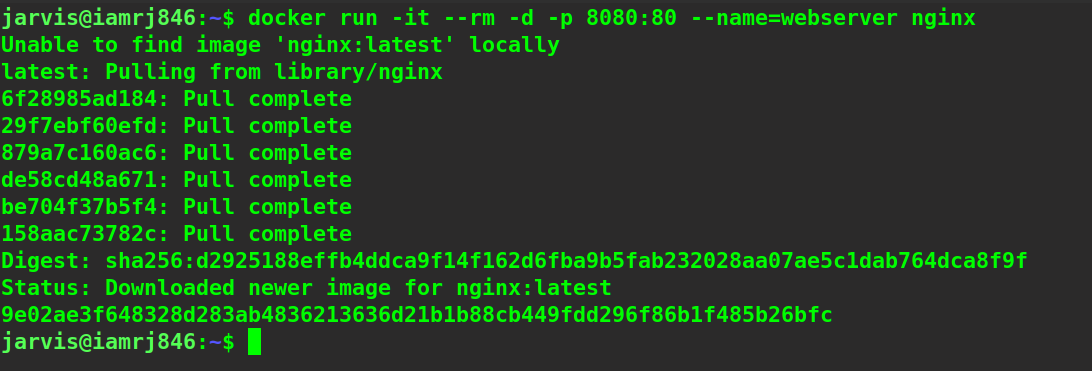
Here, if the daemon does not find the image already existing on your machine, it will try to pull it from the docker hub. If the command returns the container ID, it means that your container is actively running in the background mode.
Let’s verify by listing all the active containers.
$ docker ps
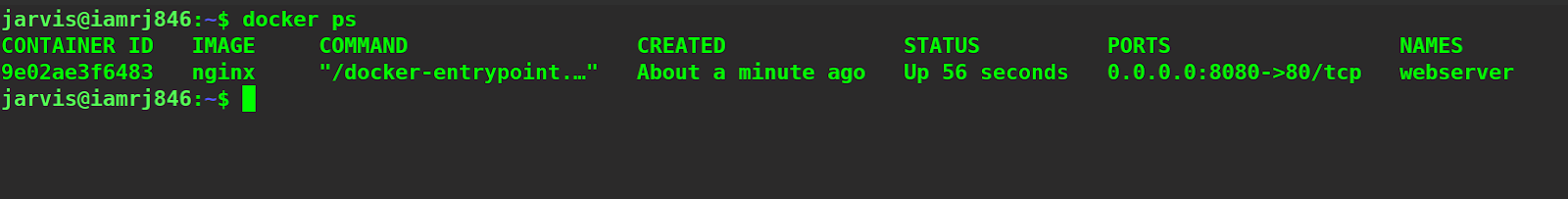
You can see that the container is actively running. If we navigate to the link localhost:8080 inside a browser, we will find the welcome page of the Nginx web server.
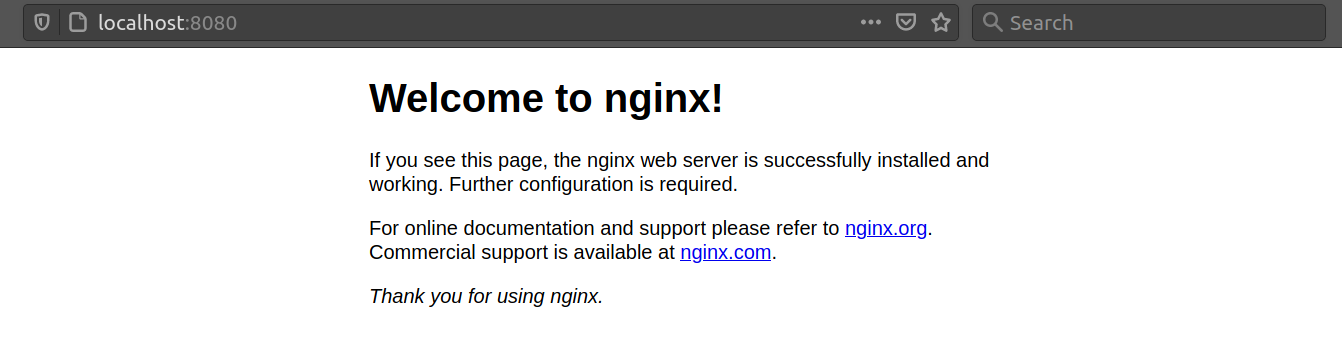
Method 2: Hosting a Static Website in Nginx Server
Now, let’s try to host a simple HTML page on an Nginx server inside a Docker Container. To do so, we will need to mount a directory in our local machine which contains the HTML files as a volume to the path /usr/share/nginx/html inside a Docker container. This is so because the Nginx Web server by default looks at this directory for files to be served. We can mount a directory as a volume using the -v option.
Have a look at the command below.
$ docker run -it --rm -d -p 8080:80 --name=webserver -v ~/Desktop/webserver:/usr/share/nginx/html nginx
In the command above, we have used the -v (volume) option to specify a source directory called webserver that needs to be mounted on the path /usr/share/nginx/html inside the container. All the files inside the webserver directory in our local machine will be copied to this path inside the container. Right now, we will create a simple HTML file with a paragraph tag containing a message.
The directory structure is -
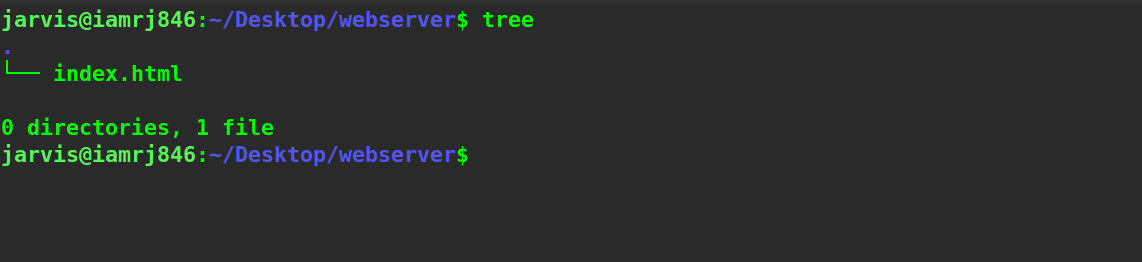
And the content of the HTML file is -
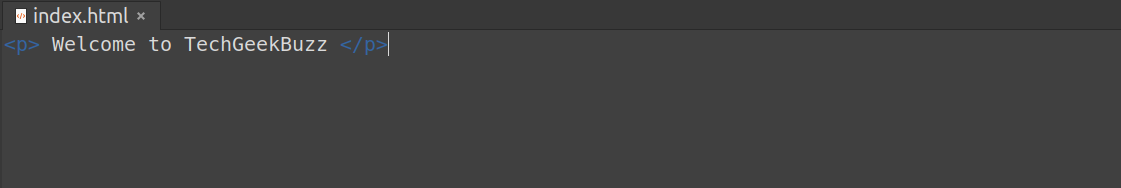
Let’s execute the above-discussed command. Before that please make sure that you have removed the previous container, else it would return an error. To remove the container, you can use the following command.
$ docker rm -f webserver
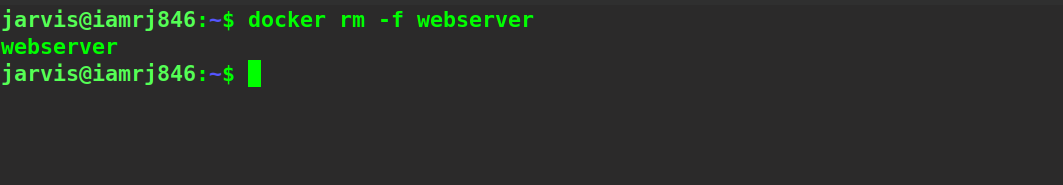
Now, we will execute the Docker run command. To verify, let’s list all the active containers as well.
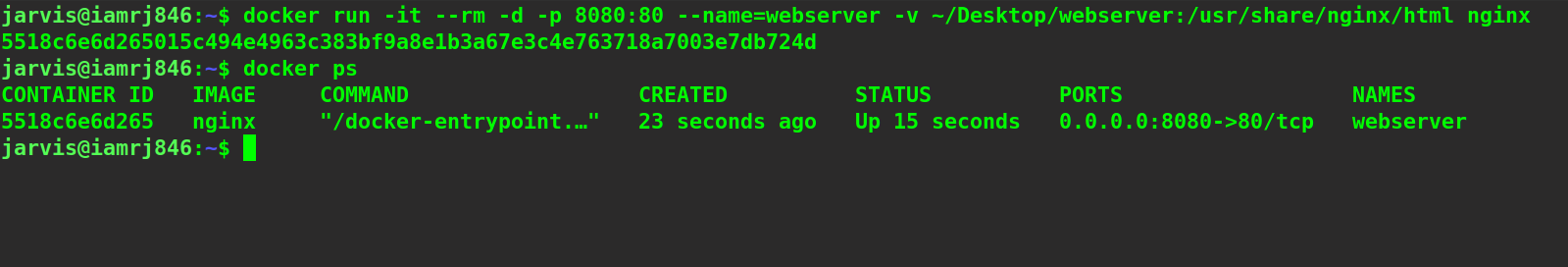
You can see that the container is actively running. Let’s navigate to the localhost:8080 address inside a browser.

Method 3: Using Dockerfile to host a static site in Nginx Server
Now, instead of directly mounting a volume on the go with the Docker run command, let’s create a Dockerfile and specify appropriate instructions there.
FROM nginx:latest COPY ./index.html /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
In the above Dockerfile, we have used the FROM instruction to pull an Nginx image with the latest tag from Dockerhub. We have used the copy instruction to copy the HTML files in the current directory in the local machine to the path /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html in the container.
The content of our build context is -
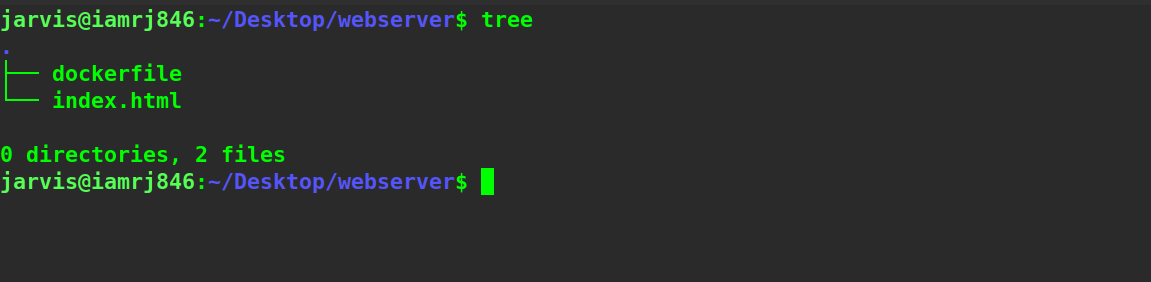
Let’s try to build this image using the Docker build command inside the same directory. We will name our image webserver.
$ docker build -t webserver .
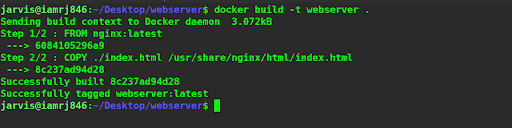
You can see that the image has been created successfully. Now. let’s use the Docker run command to run a container associated with it.
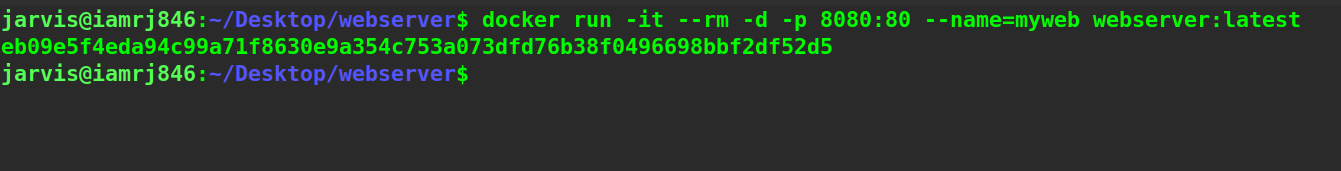
$ docker run -it --rm -d -p 8080:80 --name=myweb webserver:latest
Here, we have used the -d option to run the container in detached mode and the -p option to publish ports. We have named the container myweb.
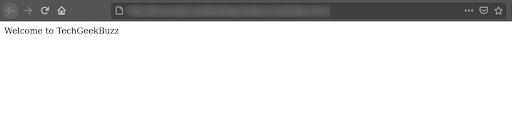
Let’s navigate to the localhost at port 80. You will find that the same HTML page has been deployed inside the Nginx server once again.
Wrapping Up!
To conclude, in this article, we have discussed three different ways to run an Nginx Web Server inside Docker containers. We discussed a plain and simple method using the Docker run command to directly run the server. Also, we discussed how to run static sites on the Nginx Web server running as a container using a Dockerfile and by mounting volumes through the Docker run command.
We hope that you will now be able to host your own website inside Docker containers by leveraging the Nginx Docker image to create a web server.
Happy Learning!
People are also reading:
- Python Client Library API for Docker
- How to pull Docker Images?
- Introduction to Docker Logging
- How to build Docker Images?
- How to copy files to and from Docker containers?
- What is Docker Container Linking?
- How to run MySQL in Docker Containers?
- How to create a private registry for Docker?
- Docker Storage Drivers
