A scanner is an input device that scans an image, text, and any other document and converts it into a digital format. This digital document can be later viewed on a computer system.
Simply put, a scanner is a hardware device that converts any hard copy into a soft copy or digital format. It works completely in opposition to a printer, which converts digital documents into hard copies.
Scanners leverage various technologies, such as optical character recognition (OCR) and magnetic ink character recognition, to scan physical images and text and convert them into digital information.
They are primarily found in offices, as they help eliminate the storing of information on paper. Over time, a lot of paper files get accumulated. Also, the ink on the paper may fade away if it’s too old. Many papers may get lost due to negligence.
However, scanners help store all physical documents electronically on a computer. Further, you can store digital documents on cloud storage to prevent them from getting deleted accidentally.
This blog post aims to help you get acquainted with some common types of scanners available out there. After reading this article, you will be able to differentiate each type of scanner and choose the right one for your needs.
8 Different Types of Scanners with Examples

|
Type of Scanner |
Description |
|
Flatbed Scanner |
|
|
Sheetfed Scanner |
|
|
Drum Scanner |
|
|
Negative Scanner |
|
|
Iris Scanner |
|
|
Handheld Scanner |
|
|
Barcode Scanner |
|
|
Fingerprint Scanner |
|
|
Book Scanner |
|
Have a look at some of the most common types of scanners with examples.
1. Flatbed Scanners

Flatbed scanners are widely used types of scanners with a simple and sleek design. They are commonly found in homes and small offices. They are often referred to as desktop scanners or personal computer scanners.
These scanners have a flat, glass surface to hold a sheet of paper. The flip-flop cover protects the glass surface from getting crushed or damaged. You can easily place A4-size documents on a flat surface for scanning. Sheet feeders in flatbed scanners support scanning multiple sheets of paper.
Flatbed scanners work with flat objects, such as paper or photographs. It also supports open books to be placed over the flat glass surface.
Examples:
- Epson Perfection V39 Scanner
- Canon LIDE300 Scanner
- Epson WorkForce Flatbed Doc Scanner
2. Sheetfed Scanners

Sheetfed scanners are also known as document scanners or automatic document scanners. They come with an automatic document feeder where you can feed multiple sheets to scan them in one go. They are known for their precision and can scan any document or photograph.
However, it is important to remember that this type of scanner does not support scanning bulkier objects, like books. Instead, it scans stacks of papers and unbound documents quickly.
Sheetfed scanners are primarily used in offices because of their ability to scan large volumes of sheets in a single pass. They can scan 50 to 500 sheets of paper and are multiple times faster than flatbed scanners.
Examples:
- HP Sheet-feed Desktop Scanner (L2759A)
- HP Scanjet Pro 2000 s2 Sheet-Feed Scanner
- Epson Workforce DS-870 Sheetfed Scanner
- Fujitsu ScanSnap S1300i Sheetfed Scanner
- Canon P-215II Document Scanner
3. Drum Scanners

A drum scanner is a type of scanner consisting of a cylindrical drum in which a photograph or paper is wrapped around. When the drum rotates at a speed of 1000 revolutions per minute (RPM), the moving detector head scans the photograph or paper longitudinally.
Drum scanners are well known for capturing or scanning high-resolution images. They leverage a photomultiplier tube (PMT), which is highly sensitive to light, for scanning images or documents. This tube can produce resolutions of more than 10,000 dpi. Hence, every intricate detail in an image or document is scanned correctly and with high resolution.
Book publications and printing presses primarily use drum scanners due to their scanning quality.
Examples:
- ICG's model 370
- Heidelberg ChromaGraph S3900
4. Negative Scanner

A negative scanner is a type of scanner that allows you to scan negatives and films and reproduce them on computers as images. It significantly saves the time and effort required to capture photographs in dark rooms.
Negative scanners come with an adapter or placeholder to hold a negative or film. Place a negative into a negative scanner and use editing software like Adobe Photoshop to import images into a computer. Further, this tool will enable you to edit images the way you want, like crop, adjust lighting, add effects, etc.
Nowadays, negative scanners are used only if any old images or photographs are to be printed in newspapers.
Examples:
- Kodak Slide N SCAN Film and Slide Scanner
- Plustek OpticFilm 8200i
- Magnasonic All-in-One 24MP Film Scanner
- Canon CanoScan 9000F MKII Scanner
5. Iris Scanners
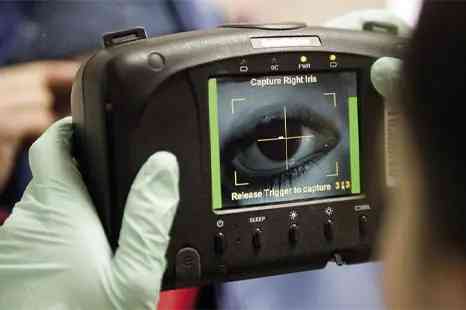
Iris scanners are a type of scanner used for biometric authentication by scanning the iris and retina of a human eye for identification. The iris has distinctive patterns unique to each human. Iris scanners scan those iris patterns, which are digitized and stored in a computer to validate the identity of a specific person.
As a result, iris scanners are considered biometric devices and are often used in Aadhaar authentication.
Examples:
- Mantra MIS100 IRIS Scanner
- BMT20 Dual Iris Scanner
- IriShield MK2120 UL Iris Scanner
6. Handheld Portable Scanners

A handheld scanner is a small, portable device that fits in a hand used to scan documents and convert them into digital information. It is among the most common input devices of a computer .
Simply take this scanner in your hand and move it over the material you want to scan. However, it is important to keep the scanner straight to avoid any kind of distortion. Hence, you must have enough experience to use a handheld scanner if you are scanning important documents.
You can scan multiple items using a handheld scanner, such as an image, magazine, plastic ID, newsletter, card, etc. The foremost advantage of handheld scanners is that they are compact and scan items that flatbed scanners cannot fit inside them. However, the major drawback is that they offer a low-quality resolution.
Example:
- Microware iScan Handheld Scanner
6. Barcode Scanners

You might have already come across barcode scanners while you shop in a mall or issue/return a book in a library. A barcode scanner, or barcode reader, is a specialized scanner designed to scan printed barcodes, decode the data they contain, and store it in a computer.
Every barcode scanner comprises a scanner, decoder, and a cable to connect with a computer where the decoded data is displayed. It automates the information collection process, reducing potential human errors. In addition, it facilitates several tasks, such as inventory tracking, asset management, and point-of-sale transaction monitoring.
You can connect a barcode scanner to a computer using a serial port or keyboard port. The scanner directs a beam of light across the barcode and measures the amount and pattern of light reflected. In short, it converts light energy into electrical energy.
Examples:
- iBall WBS-650MV Wireless Barcode Scanner
- TVSE BSC 101 Bar Code Scanner
- Pegasus PS1146A 1D Barcode Scanner
7. Fingerprint Scanner

A fingerprint scanner is yet another type of scanner used as a biometric device for authentication and identification. It scans an individual's fingerprint, converts it into an image, and stores it in a system for identification.
Fingerprint scanners are typically found in colleges and universities for the attendance of staff, mobile devices, smart locks, forensic applications, and financial transactions.
Examples:
- REALTIME FM220U Fingerprint Reader
- Mantra’s MFS100 V2 Fingerprint Scanner
- Mantra’s MAPRO OX Fingerprint Scanner
8. Book Scanner

A book scanner is a specialized type of scanner designed to scan books and generate their electronic copies. This type of scanner comes with a special placeholder to place a book below the scanner. It scans a book thoroughly and generates a copy with high-quality, readable text. The only thing a book scanner requires is manual flipping of a book under scanning.
Examples:
- CZUR Aura X-P Scanner
- IRISCAN DESK 5
Conclusion
These were some of the most common types of scanners available in the market. Flatbed, sheetfed, handheld, and drum scanners are general-purpose scanners used to scan images, documents, and any other material. In contrast,
- An iris scanner scans the patterns of an iris.
- A fingerprint scanner scans an individual’s fingerprints.
- A negative scanner scans a film or negative.
- Book scanners scan books and other text-based documents.
- A barcode scanner scans the letters embedded inside the barcode.
Hence, it is very clear to pick a type of scanner based on your requirements. We hope this article helped you understand the types of scanners.
People are also reading:


![What is an Assembler? [Definition, Working, & Types]](/media/new_post_images/What_is_Assembler.jpg)
![What is I/O? [Types, Examples, & Methods]](/media/new_post_images/What_is_I_O.webp)

Leave a Comment on this Post