A computer has different types of storage mediums categorized into two major types – primary and secondary memory . Some storage devices store data temporarily and lose it when the power supply is turned off. Meanwhile, some devices retain data permanently, even in the case of power failure. One of the types of memory that store data permanently is ROM (Read-Only Memory).
ROM is a primary, non-volatile memory holding its content persistently, irrespective of the power supply.
When we talk about ROM, we generally have a perception of a memory type that does not support writing data. However, some types of ROM, such as EPROM and EEPROM, support erasing existing content and writing new ones to ROM.
This blog post aims to make you aware of the different types of ROM available and their functions.
So, let us get started!
What is ROM (Read-Only Memory)?
ROM stands for Read-Only Memory. It is a type of primary memory that generally stores instructions and programs that rarely change throughout a system’s life cycle. It is a non-volatile memory holding instructions required for a computer's booting process (the start process). It also stores firmware for several hardware devices, including the startup firmware.
Firmware: A firmware is a microcode or program loaded inside a hardware device’s memory to help it operate correctly.
As the name suggests, read-only memory allows only the reading of data and not writing data, unlike Random Access Memory (RAM). However, being a non-volatile memory, ROM always retains its data even if the power supply is cut.
Besides computers, ROM is used in many devices, including gaming consoles, laser printers, calculators, and optical devices like CDs.
Types of ROM
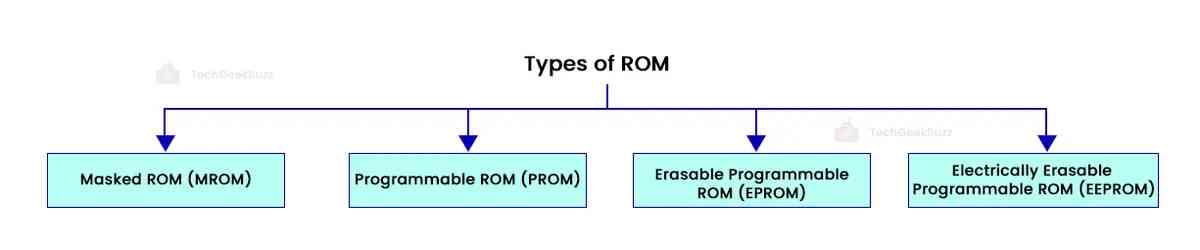
Primarily, there are four types of ROM –
- Masked ROM (MROM)
- Programmable ROM (PROM)
- Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM)
- Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM (EEPROM)
Let us discuss them in detail below.
1. Mask ROM (MROM)
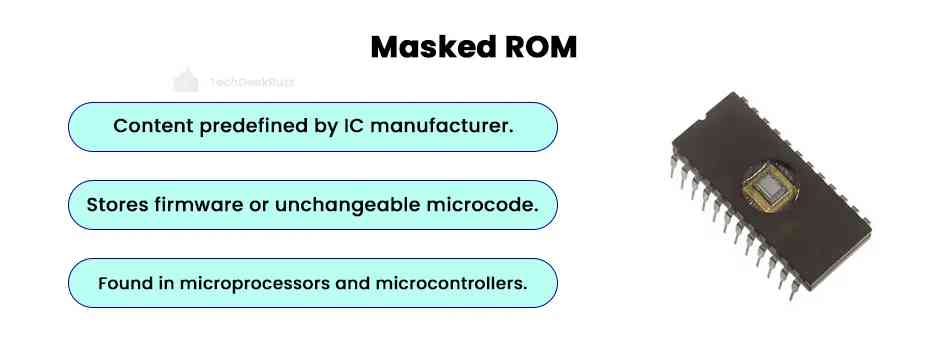
Mask ROM (MROM), or Masked ROM, is a type of ROM whose content is written by an integrated circuit (IC) manufacturer and not by users. The process of writing data to masked ROM is referred to as masked programming.
The term ‘mask’ refers to a small electronic circuit in an IC used to process data. Opaque plates called photomasks generally cover the mask in the IC. These photomasks have holes, allowing light in some specific spots while the remaining area refrains from the light. This creates different patterns and prevents others from duplicating the product.
- Some integrated circuits only contain mask ROM, while others may also contain other devices.
- Users cannot change the contents of the mask ROM. Hence, it is generally used to store firmware or any other microcode that does not require modifications.
- Most microprocessors have mask ROM to store microcode, while microcontrollers use it to store bootloader or firmware.
- Samsung Electronics, NEC Corporation, Oki Electric Industry, and Macronix are four major companies that produce mask ROM as of 2023.
The primary advantage of mask ROM is that it is less expensive than other semiconductor memory types. The reason is due to its small size.
2. Programmable ROM (PROM)
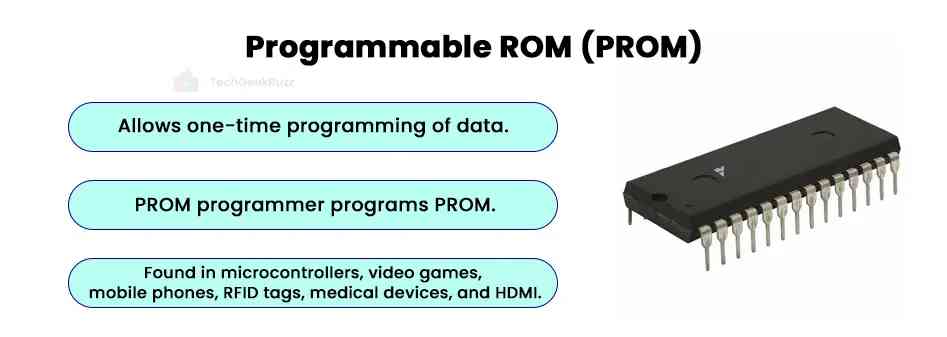
A programmable read-only memory is a type of ROM whose contents can be changed/programmed only once after manufacturing a storage device . Once changed, you cannot modify the contents of PROM anymore. Hence, PROM is also referred to as one-time programmable ROM (OTP ROM).
- The primary difference between Mask ROM and PROM is that data in Mask ROM is programmed during device manufacturing.
- On the other hand, the data in PROM is programmed after a device is manufactured.
- As a result, PROM chips are manufactured blank. After that, blank PROMs are programmed using a PROM programmer.
- Microcontrollers, video games, game consoles, mobile phones, radio-frequency identification tags, implantable medical devices, and HDMI frequently use PROM.
- OTP ROM or PROM is used in applications that require consistent and reliable reading of data.
- It provides a memory structure with a small area footprint and consumes less power.
Many modern digital devices use PROM to store data that needs no alterations, like firmware or microcode.
PROM chips initially come with all bits as ‘1’. While programming, all bits that need to be changed are burned or etched to attain ‘0’. If an error occurs while programming a PROM chip or it needs to be updated, the chip is discarded, and a new chip is used.
3. Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM)

Erasable Programmable ROM is a type of read-only memory whose contents can be erased and reprogrammed multiple times without replacing the chip. EPROM uses a strong ultraviolet (UV) source to erase the contents.
The rays are passed through a window designed on a memory chip. This process of erasing data is called burning. It leverages a special device called EPROM programmers to erase data that plugs into an EPROM burner.
- EPROMs are enclosed in a transparent fused quartz window on the top of the device. This allows the ultraviolet light to fall on the memory chip to erase contents.
- The transparent quartz window is covered with an opaque label to avoid accidental erasure of data on EPROM. This is because natural sunlight also contains some essence of UV light . In the case of strong sunlight, the UV light falling on the transparent window can erase data on EPROM. Hence, it is called UV-EPROM.
- A programmed EPROM can retain its data for 10 to 20 years. Some EPROM chips retain it for more years.
- Another type of EPROM available is one-time EPROM. It does not have a transparent quartz window for UV light to reach the silicon chip. It uses X-Rays to erase contents.
Early PC BIOS chips were EPROM. The transparent window was covered with a BIOS publisher’s name, the BIOS revision, and the copyright notice with an adhesive label.
EPROM chips generally consume more power and are more expensive than ROM and PROM. The primary disadvantage of EPROM is that it cannot erase data byte by byte. Instead, it erases or reprograms the entire data at once. Erasing and reprogramming takes a lot of time, depending on the quantity of data.
4. Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM (EEPROM)
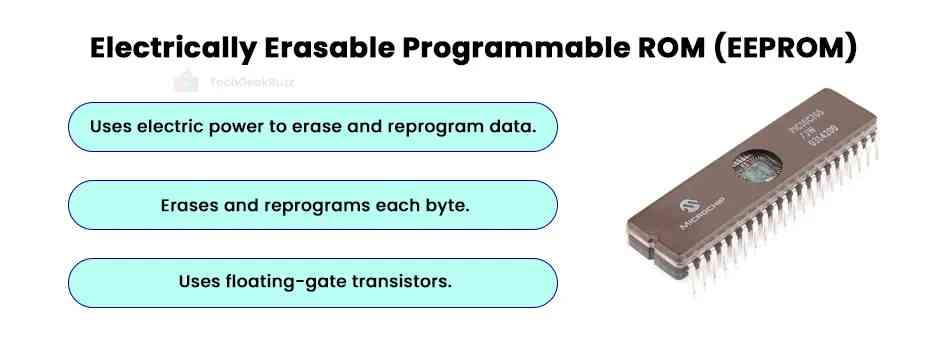
EEPROM or E2PROM is another type of ROM whose contents can be erased and reprogrammed electrically. Unlike EPROM, EEPROM enables users to erase and reprogram individual bytes of data. As a result, it is also referred to as a byte-erasable chip.
- Before the advent of EEPROM, EPROM chips were widely popular. However, its drawbacks led to the development of EEPROM chips. These chips are a collection of floating-gate transistors.
- Originally, EEPROMs were very slow, as they supported single-byte operations. They supported a limited number of erasing and programming.
- Modern EEPROMs are faster due to multi-byte page operations. They now support millions of operations.
The following are the two major types of EEPROM:
-
Electrically Alterable Read-Only Memory (EAROM)
EAROM supports the erasing and programming of data one bit at a time. The writing process in EAROM requires a lot of time and high voltage compared to the read operation. Hence, it is useful in applications that require infrequent and partial rewriting.
-
Flash Memory
Flash memory is a modern type of EEPROM, which supports faster reading and writing of data. Many new designs of flash memory offer high endurance, i.e., more than 1,000,000 cycles. NAND and NOR flash memory are two types.
The foremost advantage of EEPROM is that it can be reprogrammed multiple times without replacing the chip. The use of electric voltage erases data instantaneously. However, EEPROM is more expensive than other types of ROM and has limited data retention time.
Conclusion
This was all about the types of ROM. Read-only memory is a type of non-volatile memory that retains its data even after a power cut. It holds data that needs modifications rarely or never, like firmware or microcode.
Masked ROM, PROM, EPROM, and EEPROM are four types of ROM. Each has its own characteristics and data-erasing capabilities. Masked ROM does not allow changing its content once manufactured. PROM supports erasing and programming its content only once after manufacturing.
EPROM supports erasing and programming data using UV light, while EEPROM erases and reprograms data using electric voltage. Both these types of ROM enable multiple times of data erasing and programming.
People are also reading:
![Types of ROM [Mask ROM, PROM, EPROM, and EEPROM]](/media/new_post_images/Types_of_ROM.jpg)

![What is an Assembler? [Definition, Working, & Types]](/media/new_post_images/What_is_Assembler.jpg)
![What is I/O? [Types, Examples, & Methods]](/media/new_post_images/What_is_I_O.webp)

Leave a Comment on this Post