An Error is an illegal operation that sometimes leads to the abnormal working of code or code failure, there are many types of error defined in computer science. An exception is an event we can also call an error, but an exception only occurs during the execution of the program, these are also known as runtime errors. And exception handling is a mechanism that handles runtime error so the flow of the program does not disrupt. JavaScript also provides the mechanism for exception handling which is similar to the if...else statements, where if an exception occurs in a specific block, we execute another block of code to handle that error.
JavaScript Error or Exception handling
JavaScript provides 4 keywords that represent a block of code using curly brackets to handle exceptions or errors.
- try
- catch
- throw
- finally
The
try
block represents the code block that possibly contains any error. The
catch
block represents that code that should execute if the
try
block has an error. In simple word, it handles the error if there is an error in
try
block. The
throw
block allows us to create a custom error. We can use
throw
to tell the user about our own error messsage. The
finally
block always gets executed after the
try
or
catch
block. It is an optional code block.
1. JavaScript try and catch
The
try
and
catch
block are always used together like
if
and
else
statements. The
try
statement or block contain the main code that may have some exception or error during execution. The
catch
block allow us to define a block of code that should be executed when there is an error in the
try
block.
try and catch syntax
try {
//try code block
}
catch(err) {
//catch code block
}
try and catch in action
Now let's see how the
try
and
catch
statements works. Now we will write an error code in
try
block and to handle that error we will write some console error messages in the
catch
block.
<script>
try
{
console.logg("Hello World welcome to tecgheekbuzz"); // error
}
catch(err)
{
console.log("There is some error in the try statement");
}
</script>
Output(console)
There is some error in the try statement
In the above example inside the
try
block the
console.logg()
function created an error because there is no such
console.logg()
function in JavaScript. When the JS engine finds the error in the try block it automatically executed the
catch
block. And in output, we receive catch console print. The
err
statement in the
catch(err)
is the actual error message, if you want you can also print it on the console using
console.log()
function.
2. JS throw errors
Whenever the JavaScript engine or interpreter detects an error it stops executing the further statements. Although many of the errors are predefined inside the JS engine, but using the
throw
keyword we can create our own error.
Syntax
throw "error message"
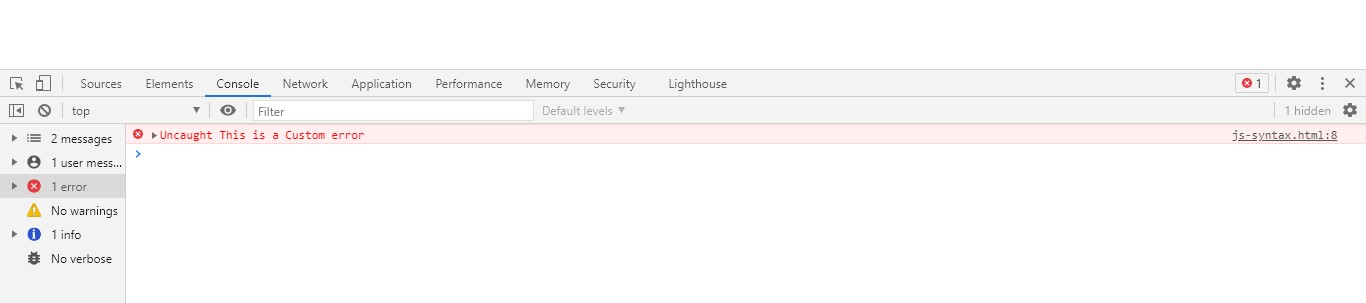
Whenever the JS interpreter executes the throw statement it throws a custom error with the throw error message and stops the execution of the program there only. Example
<script>
console.log("Hello World");
throw "This is a Custom error";
console.log("Hello World");
</script>
Output
you can see the output on the console window error section.
3. JS finally statement
The
finally
is also a block of code, it is an optional block that used after the
try
and
catch
statement. And it gets executed anyhow after the complete code execution of
try
or
catch
block.
Syntax
try {
//try block
}
catch(err) {
//catch block
}
finally {
//finally block
}
Example
<script>
try
{
console.logg("Hello World welcome to tecgheekbuzz"); // error
}
catch(err)
{
console.log("There is some error in the try statement");
}
finally
{
console.log("This statement will execute anyhow")
}
</script>
Output(console)
There is some error in the try statement This statement will execute anyhow
Summary
- Exceptions are the errors that occur during runtime.
- try block represents the code that may contain exceptions.
- The catch block represents the code that should handle exceptions of the try block.
- Using the throw keyword we can throw custom errors.
-
The
finallystatement used after the catch statement executes regardless of the try and catch statements.
People are also reading:
