Today, almost every business has two or three solutions to protect against cyber threats , including a firewall, email filtering, or antivirus. These are the key defenses that previously had you completely covered but are now insufficient to counter the increasingly severe cyber threats.
Protective measures are in place to keep out the objects you have set up to block. But what about the things that we are unaware of? How can you counter those? It seems evident what the solution is. A crew that is available around-the-clock and capable of regularly updating your security perimeter against emerging threats is a need. This is where the Security Operations Center (SOC) comes into play.
In this blog post, we shall make you familiar with everything you need to know about Security Operations Center (SOC).
So let's get started!
What is SOC?
A centralized department within an organization called the Security Operation Center (SOC) uses people, processes, and technology to prevent, identify, analyze, and respond to cybersecurity incidents while continually monitoring and improving the security status of the company.
An organization's SOC serves as the hub or central command post for its IT infrastructure, gathering information from all of its networks, computers, appliances, and data storage, regardless of where they may be. The rise of advanced threats highlights the importance of gathering context from various sources. In essence, the SOC serves as the correlation point for all events logged within the monitored company. The SOC should be responsible for choosing approaches to responding to or handling these occurrences.
How Does a SOC Work?
Most SOCs use a hierarchical approach to tackle security issues, classifying analysts and engineers according to their backgrounds and experience. A typical team might be organized as follows:
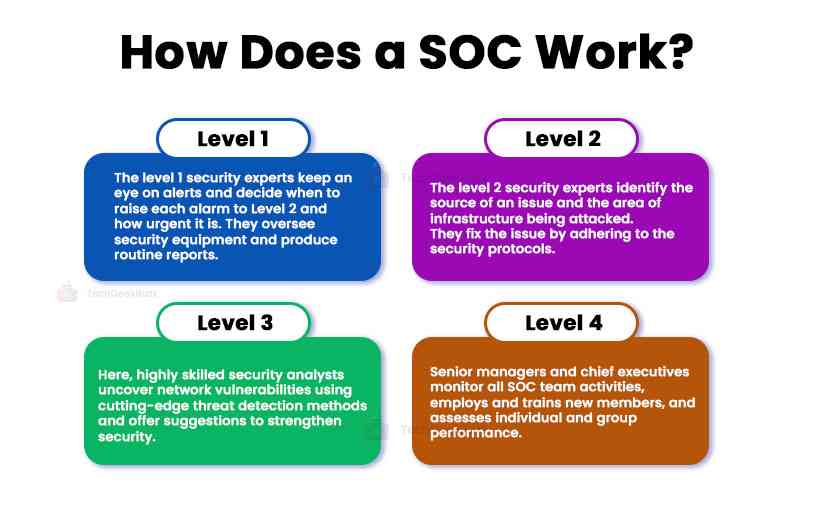
Level 1: The initial responders to an issue. These security experts keep an eye on alerts and decide when to raise each alarm to Level 2 and how urgent it is. Additionally, level 1 staff may oversee security equipment and produce routine reports.
Level 2: Due to their more incredible experience, these staff members may more easily identify the source of the issue and determine which area of the infrastructure is being attacked. They will adhere to protocols to fix the problem and clean up any spills while raising concerns for further study.
Level 3: Staff at this level consists of highly skilled security analysts actively looking for network vulnerabilities. They will identify vulnerabilities using cutting-edge threat detection methods, then offer suggestions for strengthening the organization's overall security. This group may also include specialists like forensic investigators, compliance auditors, or cybersecurity analysts.
Level 4: These senior managers and chief executives have several years of experience. This team supervises all SOC team activities, employs and trains new members, and assesses individual and group performance. During a crisis, Level 4s take over and primarily act as a point of contact between the SOC team and the rest of the business.
What Does a SOC Do? (Functions Performed by SOC)
The SOC keeps track of security information generated by the organization's IT infrastructure, including host systems, programs, networks, and security devices like firewalls and antivirus programs.
The Security Operations Center combines a variety of cutting-edge equipment with the expertise of seasoned cybersecurity specialists to carry out the following crucial tasks:
-
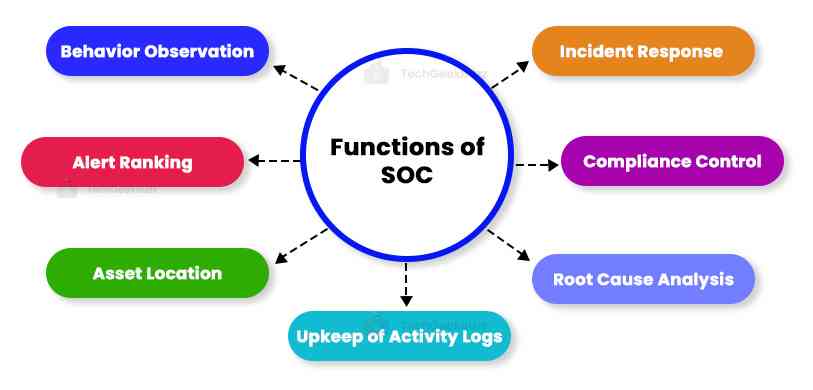
Behavior Observation
The SOC continuously monitors the IT infrastructure for anomalies. It uses proactive and reactive procedures to identify and resolve unusual activities swiftly. To reduce false positives, suspicious activity is behaviorally monitored.
-
Alert Ranking
Not every security issue is the same. A danger to an organization will vary depending on the situation. SOC teams can prioritize the most severe alerts using severity rankings.
-
Asset Locating
The SOC makes certain assets monitored for security events by developing a thorough understanding of the hardware, software, tools, and technologies used in the organization.
-
Upkeep of Activity Logs
The SOC team must keep track of all communications and activities throughout the organization. The SOC can look back and identify previous behaviors that may have led to a cyber security breach thanks to activity records. Setting a baseline for what should be regarded as usual behavior is another benefit of log management.
-
Root-Cause Analysis
The SOC may be tasked with looking into how, when, and why an incident takes place after its occurrence. It uses log data to track the source of the issue during the investigation and avoid recurrence.
-
Compliance Control
SOC team members must conduct themselves according to corporate policies, industry standards, and legal obligations.
-
Incident Response
SOC teams carry out the incident response whenever they find any compromise.
Key Security Operations Center (SOC) Team Members
Businesses of all sizes must establish an efficient security operations center (SOC). Every security team is unique, just like the businesses they work for. Businesses that value cybersecurity will make the required investments to protect their systems and data and to give their SOC team the tools they need to handle attacks.
All businesses have similar responsibilities regarding cybersecurity, although the jobs may have different names. The more typical SOC team jobs are shown below, along with the specific duties:
-
SOC Manager
The SOC manager, who leads the team, is responsible for all security activities and reports to the CISO (Chief Information Security Officer) of the company.
-
Security Analyst
Security analysts are the ones that respond to incidents initially. They are the soldiers on the front lines assessing dangers and defending against online attacks. In a nutshell, they are responsible for identifying risks, looking into them, and quickly taking appropriate action.
Additionally, analysts may be expected to carry out management-mandated security procedures as part of their duties. Further, they might contribute to organizational disaster recovery planning. Security analysts have to be available after hours to respond to emergencies in some firms.
-
Threat Hunters
Threat hunters, also known as specialist security analysts, focus on identifying and neutralizing advanced threats, brand-new or versions of existing dangers that manage to get past automated defenses.
The SOC team may include other experts depending on the firm's size or the sector it operates in.
Benefits of SOC
The primary benefit of having a SOC is the improvement of security incident detection through constant monitoring and analysis of network activity and cyber intelligence results. SOC teams can identify and address security incidents early by continuously monitoring activities throughout the organization's networks. Time is one of the significant factors in an efficient cybersecurity incident response, so this is very important.
Organizations have a significant edge in the fight to protect themselves against incidents and intrusions regardless of the source or nature of the attack because of the 24/7 SOC monitoring. With less time between the attacker's time to compromise and the time to detect, companies can better monitor threats to their environments and reduce risk.
A SOC offers a number of benefits when implemented properly, including the following:
- Monitoring and analysis of system activities and ongoing processes.
- Enhanced responsiveness to incidents.
- Reduction in the time between a compromise happening and being discovered.
- Reduced downtime
- Hardware and software asset centralization provides a more comprehensive, real-time approach to infrastructure security.
- Efficient communication and collaboration.
- Reduction in the costs directly and indirectly related to managing cyber security events.
- Customers and employees feel more confident disclosing their private information because they trust the company.
- More openness and control over security operations.
- A transparent chain of command for systems and data is essential for successfully prosecuting cybercriminals.
Major SOC Challenges and Solutions
The SOC manages all facets of the organization's digital security, an increasingly complex function. Establishing and upkeep a strong SOC can be difficult for many organizations. SOC teams must continuously keep an edge over attackers.
In recent years, this has become increasingly challenging. Here are a few difficulties that any SOC team encounters:

-
Talent Gap
Challenge: When compared to the number of open positions, there is a critical lack of cyber security experts. In 2019, there were 4.07 million vacancies for professionals. SOCs constantly balance on a thin line with a great danger of team members becoming overburdened due to the lack of resources.
Solution: To replace shortages in their SOC team, organizations should look within and consider upskilling current staff. Every position in the SOC should have a backup qualified to take over if the primary fills an unexpected vacancy. (Or learn to use the most affordable resource they can discover rather than paying what talents are worth.)
-
Massive Data and Network Traffic
Challenge: The challenge of processing all the available data in real-time is increasing due to enormous data volume and traffic growth.
Solution: SOCs use automated technologies to filter, parse, aggregate, and correlate data to minimize manual analysis.
-
Professional Hackers
Challenge: Network security is a crucial part of an organization's cyber security plan in response to sophisticated attackers. Since sophisticated players have the tools and knowledge to go over conventional defenses like firewalls and endpoint security, it requires special attention.
Solution: Implement tools with the ability to detect anomalies and learn through machine learning.
-
Emerging Threats
Challenge: Traditional signature-based detection, endpoint detection, and firewalls cannot detect unidentified threats.
Solution: SOCs can enhance existing signature, rules, and threshold-based threat detection systems by incorporating behavior analytics to uncover ordinary behavior.
-
Alert Exhaustion
Problem: Anomalies occasionally occur in various security systems. The number of notifications can become overwhelming if the SOC relies on unfiltered anomaly alerts. Many alerts could not contain the information and context necessary for an investigation, diverting teams' attention from the actual issues.
Solution: Set up the alert ranking and monitoring material to distinguish between low-fidelity and high-fidelity warnings. Use behavioral analytics tools to ensure the SOC team is concentrated on handling the most unexpected issues first.
-
Security Tool Overload
Problem: Security tools frequently lack communication with one another, have a narrow field of application, and lack the complexity to recognize sophisticated threats.
Solution: Use a centralized monitoring and alerting platform and concentrate on efficient defenses.
Conclusion
This article has explained in depth about security operations center (SOC), it works, the significant benefits, the challenges, and the solutions to resolve issues related to SOC.
In the digital and post-Covid era, most organizations face significant difficulties that the SOC product addresses. They benefit organizations of all kinds and varieties and should be considered part of any cyber security strategy.
I hope you liked the article!
People are also reading: