What is Online Analytical Processing (OLAP)
OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) is a particular category of software that allows users to analyze information from various database systems at the same time. OLAP is a type of technology that allows analysts to extract and view business data from various points of view.
The counterpart of online analytical processing systems is OLTP systems . OLTP stands for online transaction processing. Analysts usually require grouped, aggregated, and joined data. These processes in relational databases are resource-intensive. Through OLAP, you can pre-aggregate and pre-calculate data to make analysis faster and easier. It is divided into one or more extra cubes. These cubes are designed to create and view reports that become simple.
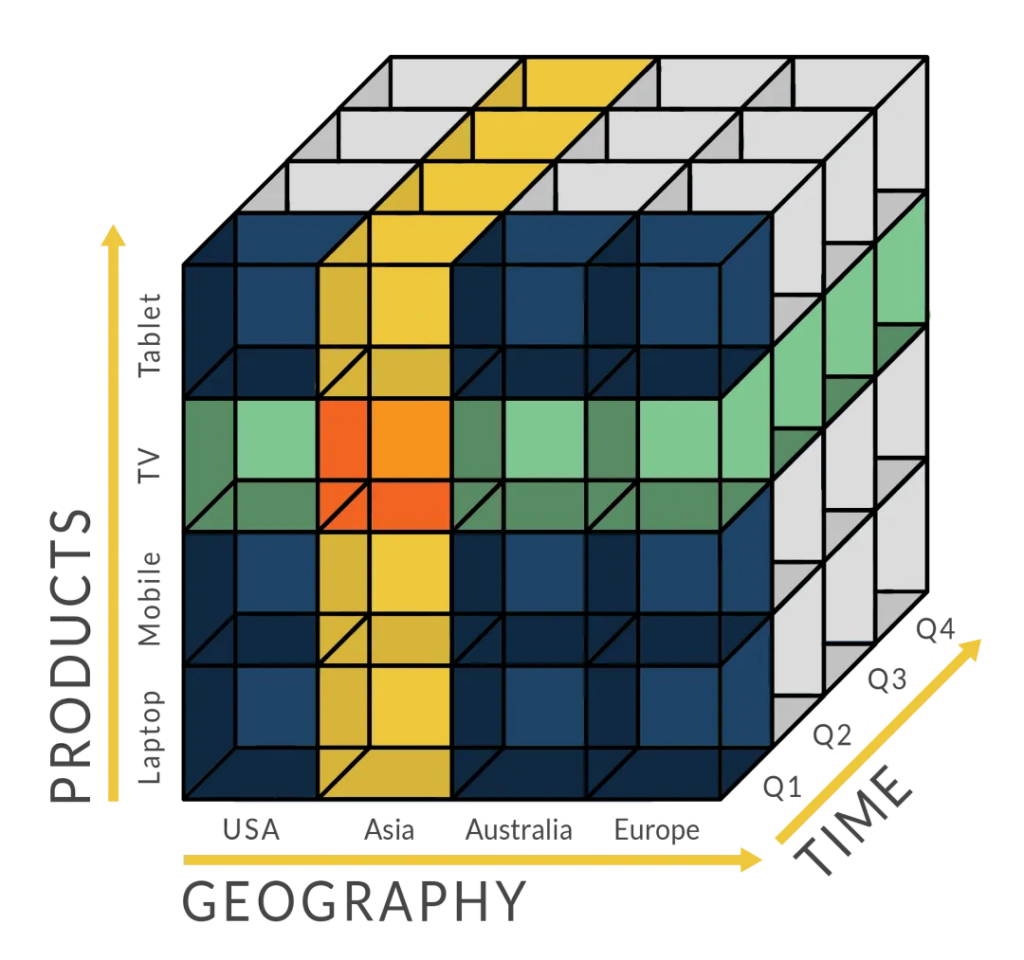
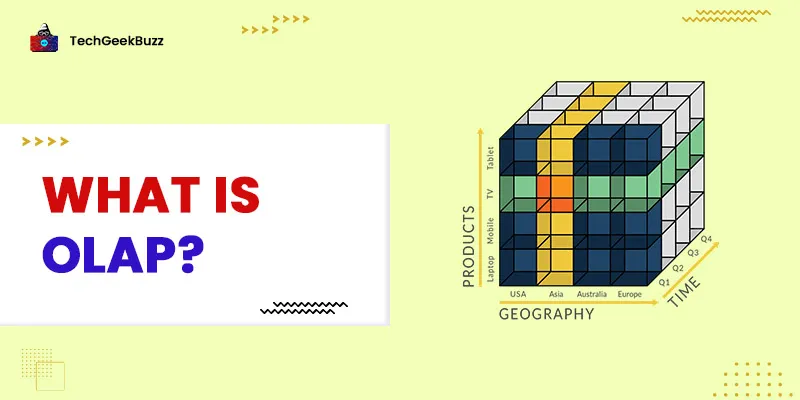
Basic Analytical Operations of OLAP
There are four types of analytical operations in online analytical processing:
1. Roll-up
It is also called consolidation or aggregation, and this particular operation can be executed in two ways:
- Decreasing dimensions.
- Climbing up the concept hierarchy, which is the system of grouping objects based on their order and level.
2. Drill-down
In the drill-down operation, data is fragmented into tinier parts, and it is the inverse of the roll-up process. Drill-down can be done through:
- Moving down the theory hierarchy.
- Developing a dimension.
3. Slice and dice
3.1 Slice
This OLAP operation selects one dimension and designs a new sub-cube.
3.2 Dice
This particular operation is related to a slice. The variation in dice is that you select two or more dimensions that result in the production of the sub-cube.
4. Pivot (rotate)
This type of OLAP operation rotates the data axes to provide a substitute presentation of data.
Types of Online Analytical Processing Systems
1. ROLAP
ROLAP is relational online analytical processing. It runs with data that exists in the relational database. Dimensions and fact tables are saved as relational tables. ROLAP also provides a multidimensional analysis of data and is the fastest-growing type of OLAP system. ROLAP refers to an extended RDBMS with multidimensional data mapping for performing the standard relational operations.
Advantages of ROLAP
- High data efficiency: It offers high data efficiency due to query performance, and access language is individually optimized for multidimensional data analysis.
- Scalability: It is a type of OLAP system that offers scalability to manage a large volume of data even when the data is continuously growing.
Drawbacks of ROLAP
- High resource demand : It needs a high utilization of manpower, hardware, and software.
- Aggregate data limits : ROLAP tools utilize SQL for calculating total data, but there is no set limit for dealing with computation.
- Slow query performance : It is slower in this model when compared with MOLAP.
2. MOLAP
The full form of MOLAP is multidimensional online analytical processing. It utilizes array-based multidimensional storage engines for displaying multidimensional views of data. Basically, MOLAP systems use an OLAP cube.
3. HOLAP
Hybrid OLAP is a combination of ROLAP and MOLAP. This provides faster computation of MOLAP and higher scalability of ROLAP. HOLAP uses two databases. The data collected or calculated is saved in the multidimensional OLAP cube. Detailed information is stored in a relational database.
Advantages of Hybrid OLAP
- This type of OLAP helps reduce disk space and also remains compact, which helps avoid issues related to access speed and convenience.
- Hybrid OLAP uses Cube technology that allows faster performance for all types of data.
- ROLAP is updated immediately, and HOLAP users have access to instantly updated data in this real-time system. MOLAP brings data cleanliness and conversion to the system, which improves data relevance. Hence, HOLAP brings the best of both worlds.
Drawbacks of Hybrid OLAP
- Higher complexity level : The major drawback of HOLAP systems comes from the fact that it supports both ROLAP and MOLAP tools and applications. Thus, it complicates the system.
- Potential overlaps : Especially their functionalities are more likely to be overlapping.
4. DOLAP
DOLAP stands for desktop OLAP. A user downloads a portion of data from a database locally or analyzes it on their desktop in the desktop OLAP. DOLAP is relatively inexpensive to deploy because it offers very limited functionality compared to other types of OLAP systems.
5. WOLAP
Web OLAP is an OLAP system accessible through a web browser. A WOLAP system follows a three-tier architecture. It consists of three components, namely the client, middleware, and database server.
6. Mobile OLAP
Mobile OLAP enables users to access and analyze OLAP data using their mobile devices.
7. SOLAP
SOLAP (Spatial OLAP) facilitates the management of both spatial and non-spatial data in a Geographic Information System (GIS) .
Benefits and Limitations of Online Analytical Processing
Benefits of OLAP
- It is a stage for all types of businesses that includes planning, budgeting, reporting, and analysis.
- Information and computation are compatible with an OLAP cube, and it is a significant benefit.
- It quickly analyzes "what if" scenarios.
- Users can quickly search OLAP databases for broad and specific terms.
- OLAP provides a building block for data mining tools , business modeling tools , and performance reporting tools.
- It enables users to slice and dice cube data by different dimensions, measures, and filters.
- Online analytical processing is good for analyzing time series.
- Some clusters and outliers are easy to find with OLAP.
- It is a robust visual online analytical processing system that offers quicker response times.
Limitations of OLAP
- OLAP needs data to be organized into a snowflake schema , which is complex in implementation and administration.
- You cannot have a huge number of dimensions in a single OLAP cube.
- Users cannot access transaction data from an OLAP system.
- Any modification to the OLAP cube requires a full update of the cube, which is a time-consuming process.
Conclusion
Online analytical processing is a type of technology that allows analysts to extract and view business data from various points of view. Analysts need to be grouped, aggregated, and joined data. These operations in the relational database are resource-intensive. Hence, an OLAP system makes life easier for analysts to get data in the required form.
People are also reading: