The number of endpoints connected to networks has dramatically increased for almost all businesses. This means that any device that employees use to connect to a company's network creates a potential risk and an entry point that threat actors can take advantage of to carry out their data breaches. There are increasingly IoT-enabled systems in smart factories and smart cities in addition to consumer devices like desktops, laptops, and smartphones.
As a result, it becomes essential for organizations to deploy solutions that protect endpoints and maintain their cybersecurity posture. This is where endpoint security comes into play. Endpoint security ensures that endpoints or end-user devices are safe against cyber threats .
In this article, we'll explain what an endpoint is, how endpoint security works, and what is the core functionality of an endpoint protection solution.
What is Endpoint Security?
Endpoint security is a practice of preventing malicious hackers and organizations from taking advantage of entry points of end-user devices, such as PCs, laptops, and mobile devices, to fulfill their malicious intent. Endpoint security systems shield these endpoints from different types of cyberattacks and threat actors, whether on a network or in the cloud.
The endpoint security solution provides comprehensive protection against cyberattacks and dynamic zero-day threats. It creates a cutting-edge platform that significantly aids businesses by combining numerous attack prevention, detection, and response technologies with intelligent services:
- Discover, disrupt, prevent, and identify malicious attacks, stop them in their tracks, and prevent them from doing any lasting harm.
- Track and observe to find and block intrusions, keep an eye on, and trace intruders' activity.
- Find the underlying causes. Identify the risks' underlying motivations.
What is Considered an Endpoint?
Endpoints are now the most popular method of computation and communication across networks and devices in today's digitally empowered enterprises. But what exactly is an endpoint?
An endpoint is a device that connects to the computer system from outside the firewall. The following examples are the examples of endpoints:
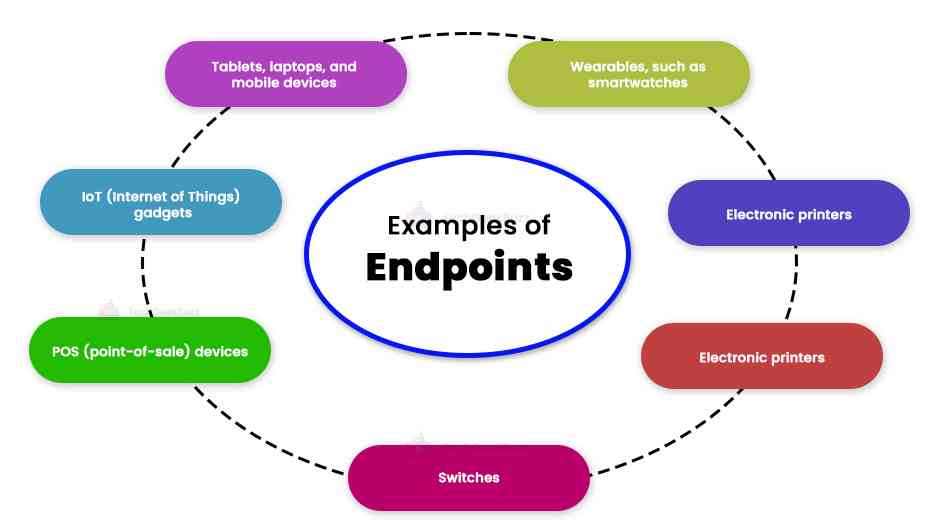
- Tablets, laptops, and mobile devices
- IoT (internet of things) gadgets
- POS (point-of-sale) devices
- Switches
- Electronic printers
- Wearables, such as smartwatches
- Other connected devices to the centralized network
Endpoints serve as essential, vulnerable ports of entry for cybercriminals. Attackers run code on endpoints and use flaws to their advantage. Also, endpoints are locations for assets that can be encrypted, exfiltrated, or used. Due to the increasing mobility of corporate workforces and the increased use of off-premises endpoints around the world, endpoints have become more susceptible to cyberattacks.
How Does Endpoint Security Work?
Endpoint security safeguards the data and operations associated with the particular network-connected devices. Platforms for endpoint protection (EPP) operate by scanning files coming into the network.
Modern EPPs rely on the capacity of the cloud to hold a constantly growing database of threat information, freeing endpoints from the bloat caused by needing to store this information locally and the maintenance required to keep these databases up to date. When utilizing the cloud to access this data, speed and scalability are improved.
Let us see how endpoint security functions to protect your data and system:
- Protecting data and workflows related to all connected devices to the corporate network is the primary objective of any endpoint security solution. To accomplish this, it scans files as they enter the network and compares them to a growing database of threat data stored in the cloud.
- The Endpoint Security solution gives network or server administrators a single management panel that they may use to oversee the security of every device connecting to them. After that, client software is installed either locally or remotely on each endpoint. When the endpoint is configured, the program automatically pushes updates, authenticates login attempts made from it, and manages corporate policies.
- This solution also secures endpoints by controlling applications. This prevents the user from accessing or downloading programs that the company deems hazardous or unlawful. To avoid data loss, encryption is also used.
- With the help of the endpoint security solution, enterprises can easily find malware and other typical security concerns. The organization can identify more sophisticated threats, including polymorphic and zero-day attacks, thanks to its ability to provide endpoint monitoring, detection, and response.
Importance of Endpoint Security
A strategy for endpoint security is essential since the number of endpoints is constantly growing due to the quick shift to remote work caused by the pandemic. Every remote endpoint might serve as the starting point for an attack.
The Gallup survey found that 51% of US employees were still working remotely in April 2021, up from a majority in 2020. Endpoint hazards and the sensitive data they contain are ongoing problems.
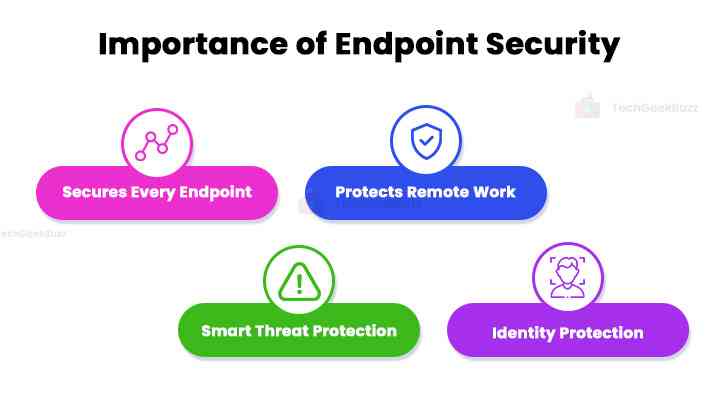
Enterprises must use endpoint security technology to protect themselves from the severe threat landscape. A few of the main advantages of an endpoint security strategy are as follows:
-
Secures Every Endpoint
Organizations must take security measures to connect employees safely as more endpoints and different devices are available nowadays. Additionally, they must guarantee that the data stored on those devices are safe and cannot be stolen or lost.
-
Protects Remote Work
Bring your own device (BYOD), and remote working rules are two examples of new work practices associated with increased device usage. Endpoint security solutions give workers the freedom to work efficiently from any location and on any device.
-
Smart Threat Protection
Hackers are using more advanced attack techniques, creating new strategies for breaking into company networks, stealing data, and coercing people into disclosing private information. Endpoint security is essential for keeping modern businesses safe and preventing hackers from accessing their networks.
-
Identity Protection
The conventional guarding of the corporate perimeter is no longer workable when employees access company systems from various devices, networks, and places. No matter when or where employees connect to corporate data and resources, endpoint security guarantees that the company puts security on their devices, allowing them to do so in a secure manner.
Endpoints exist where humans and machines converge, making endpoint protection difficult. Businesses struggle to keep their systems secure without obstructing their workers' lawful activities. Despite the effectiveness of technical solutions, social engineering attacks on employees will always exist.
Endpoint Protection vs. Antivirus
Traditional antivirus solutions and endpoint protection platforms (EPP) differ in several essential aspects. Let us have a look at a few of them:
-
Device Protection
Conventional antivirus solutions, such as those installed on laptops to keep them safe, are intended to safeguard a single device. On the other hand, endpoint security solutions aim to secure every connected device across the whole company network.
-
Threat Protection
Antivirus software shields organizations from malware in their database of known dangers. However, sophisticated attackers frequently lack a conventional signature, which could expose firms to risk. Endpoint security solutions provide a more comprehensive approach that guards against unknown dangers and threats, including data loss, signatureless malware, and phishing attacks.
-
Continuous Protection
Antivirus solutions employ a signature-based detection approach to find and safeguard organizations against potential hazards. As a result, those who have not updated their antivirus software may still be vulnerable. Endpoint security products, in contrast, connect to the cloud and update automatically, assuring that users always have access to the most recent version.
-
Advanced Internal Security
While conventional antivirus solutions can stop malware, they do not prevent employees from storing confidential information on a USB stick and taking it from the company. Through technologies like data access controls and data encryption, endpoint solutions provide improved protection against dangers like data loss and data leakage.
This guarantees that unauthorized workers cannot access data beyond the scope of their access rights and steal or sell it. Meanwhile, endpoint security uses cutting-edge technology like behavioral analysis, enabling companies to identify risks based on unusual behavior from internal and external sources.
-
Admin Control
To keep the antivirus software current with new malware risks, antivirus solutions rely on users actively upgrading the software. On the other hand, endpoint solutions offer linked security and transfer administration duties to the IT or security team. This eliminates the possibility of human error endangering the devices of end users.
-
Enterprise-Wide Control
Conventional antivirus programs often only alert users about threats when they are found. A security expert will then assess and look into the risk in person. However, the endpoint security solution offers a centralized interface that enables administrators to keep an eye on activity, set up, patch, and update software, look into any suspicious traffic, and handle problems remotely.
Additionally, it enables administrators to do these tasks simultaneously on numerous endpoints, expediting employee issue response and significantly reducing the time required by the IT and security teams.
-
Integration
An antivirus solution serves a specific function and runs as a standalone application. However, an endpoint security strategy offers the significant benefit of integration. We can think of it as a suite of several solutions that we can quickly integrate to provide more thorough security protection.
Endpoint Protection vs. Firewall
A firewall is a security system that controls access to a network by monitoring incoming and outgoing traffic. Meanwhile, endpoint security safeguards the information stored on devices connected to a network, allowing the company to monitor all staff devices and track their usage.
Earlier, firewalls were ideal for companies with all employees working from the exact location and logging into the same network. However, as more individuals work remotely or from home, a firewall is no longer sufficient because devices become susceptible to attacks as traffic bypasses the leading network.
It is essential to choose the optimal security solution depending on each firm's unique circumstances and security needs. Essential elements to consider when making this choice include:
-
The Number of Employees
A product that involves managing devices individually can just function fine for small organizations. However, it may become more challenging for IT and security teams to maintain each device in this way as they grow larger. Utilizing a security solution that centralizes endpoint control would, therefore, greatly increase their effectiveness.
-
Employee Location
Companies with employees that work from a central location might not have any problems controlling endpoint access. The problem arises when employees work from diverse locations. For enterprises with a dispersed workforce, people working from homes, remote offices, or while on the go, an endpoint security solution that secures endpoints regardless of where or when employees attempt to access their networks and resources is essential.
-
Device Ownership
Device sovereignty has become more ambiguous as BYOD usage has increased. Employees extensively leverage their own devices to sign in and log out of the business networks. Businesses may secure their staff members every time they log into their networks and constantly keep an eye on access with the help of endpoint security solutions.
-
Data Sensitivity
Companies handling sensitive information or intellectual property will find that antivirus software is insufficient to protect their data because it merely shields it from infections. These firms must implement endpoint security solutions to safeguard themselves against data loss incidents, which significantly harm their finances and reputations. They can protect their most important data, comply with regulations, and pass audits by employing endpoint security solutions.
Core Functionality of an Endpoint Protection Solution
The following are the essential components that an endpoint security solution should include with the aim of offering continuous breach prevention:
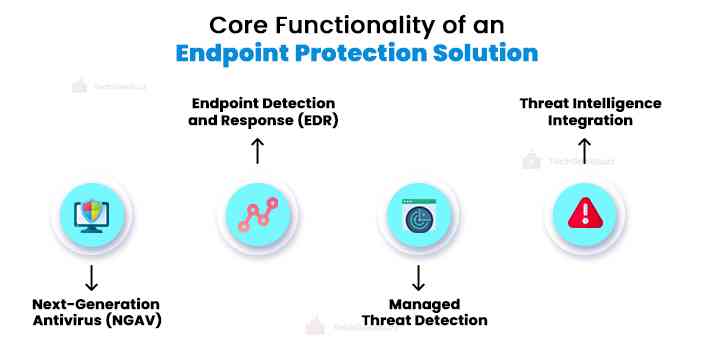
1. NGAV for Prevention
Traditional antivirus software is unable to detect more than half of all attacks. They work by comparing malicious signatures, or pieces of code, to a database that contributors update each time when they discover a new malware signature. The issue is that the database does not contain malware that has not yet been classified as known malware. When a piece of malware becomes available to the public, it takes some time before specific antivirus programs can detect it.
The next-generation antivirus (NGAV) overcomes this issue in traditional antivirus programs. They employ more sophisticated endpoint security technologies like AI and machine learning to detect novel viruses by looking at more factors, including file hashes, URLs, and IP addresses .
2. EDR for Detection
Prevention is insufficient. Because no protection is impenetrable, some attackers will always succeed in breaching defenses and entering the network. Traditional security cannot detect when this occurs, giving attackers the freedom to stay in the area for days, weeks, or months. Businesses must swiftly identify and eliminate attackers to stop these "silent failures."
To avoid silent failures, the endpoint detection and response (EDR) system must provide continuous and comprehensive visibility into what is happening on endpoints in real-time. Search for solutions that provide sophisticated threat detection, investigation, and response capabilities, such as alert triage, threat hunting, suspicious activity validation, detection, and containment of malicious behavior.
3. Managed Threat Detection
Automation alone cannot identify every attack. The ability of security experts to identify today's complex threats is crucial.
Professional teams carry out managed threat hunting to gather crowdsourced data, draw lessons from past instances and advise on how to best react whenever there is any hostile activity taking place.
4. Threat Intelligence Integration
Businesses must be aware of dangers as they evolve if they want to stay one step ahead of attackers. Because experienced adversaries and advanced persistent threats (APTs) can move quickly and discreetly, security teams require current and reliable knowledge to make sure defenses are automatically and accurately calibrated.
Threat intelligence integration should be automated to gather information in minutes compared to hours, and every incident should be investigated. To provide pro-active protection against upcoming assaults, it should produce unique indicators of compromise (IoCs) straight from the endpoints. There should also be a human component of knowledgeable security researchers, threat analysts, cultural specialists, and linguists who can understand new risks in various circumstances.
Conclusion
Endpoint protection is essential for preventing, mitigating, and resolving internal and external cyber threats. Endpoint security solutions and strategies must scale to accommodate the increasing variety of devices, whether on-premises or remote, employee- or vendor-owned. The most essential thing to remember is to incorporate solutions into your endpoint security technology stack that can interact and work with the rest of your IT and security ecosystem.
This article has covered all the aspects of endpoint security and how you should incorporate it into your systems to safeguard your data.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article!
People are also reading:
![What is Endpoint Security? [Definition, Working, & Importance]](/media/new_post_images/Endpoint_Security.webp)



Leave a Comment on this Post