Problem
Given a binary tree, return the smallest subtree that has all the deepest nodes of the original tree. The deepest node is a node having maximum depth in the tree. You only need to return the root of the output subtree in the code.
Sample Input
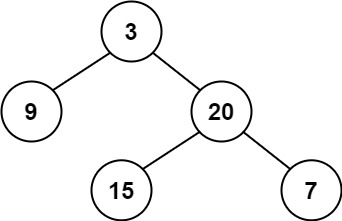
Sample Output
20
Explanation
The deepest nodes are ‘15’ and ‘7,’ and the root of this smallest subtree is ‘20’
Approach
Using DFS, traverse the Binary Tree recursively. Determine the depth of each node's left and right subtrees. Traverse the left subtree if the depth of the left subtree is greater than the depth of the right subtree. Traverse the right subtree if the depth of the right subtree is greater than the depth of the left subtree. Otherwise, return the currently selected node.
Complexity Analysis
The time complexity is O(N), and the space complexity is also O(N)
C++ Programming
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int data)
{
this->val = data;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
int getDepth(TreeNode* root)
{
if (!root)
return 0;
// If current node is a leaf node
if (root->left == NULL
&& root->right == NULL)
return 1;
return max(getDepth(root->left),
getDepth(root->right))
+ 1;
}
void solve(TreeNode* root, TreeNode*& ans)
{
if (!root)
return;
// height of left subtree
int left = getDepth(root->left);
// height of right subtree
int right = getDepth(root->right);
// If height of left subtree is more
if (left > right) {
// Traverse left subtree
solve(root->left, ans);
}
// If height of right subtree is more
else if (right > left) {
solve(root->right, ans);
}
else {
// Return current node
ans = root;
return;
}
}
int main()
{
struct TreeNode* root= new TreeNode(1);
root->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->right = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode* ans = NULL;
solve(root, ans);
cout << ans->val;
return 0;
}
Output
1
Java Programming
import java.util.*;
class Solution
{
static class TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int data)
{
this.val = data;
left = null;
right = null;
}
};
static int getDepth(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
// If current node is a leaf node
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return 1;
return Math.max(getDepth(root.left),getDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
static TreeNode solve(TreeNode root, TreeNode ans)
{
if (root == null)
return ans;
// height of left subtree
int left = getDepth(root.left);
// height of right subtree
int right = getDepth(root.right);
// If height of left subtree is more
if (left > right)
{
// Traverse left subtree
ans = solve(root.left, ans);
}
// If height of right subtree is more
else if (right > left)
{
ans = solve(root.right, ans);
}
else
{
ans = root;
return ans;
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);
root.left = new TreeNode(2);
root.right = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode ans = null;
ans = solve(root, ans);
System.out.print(ans.val);
}
}
Output
1
Python Programming
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
def getDepth(root):
if (not root):
return 0
# If current node is a leaf node
if (root.left == None and root.right == None):
return 1
return max(getDepth(root.left), getDepth(root.right)) + 1
def solve(root):
global ans
if (not root):
return
# Stores height of left subtree
left = getDepth(root.left)
# Stores height of right subtree
right = getDepth(root.right)
# If height of left subtree is more
if (left > right):
# Traverse left subtree
solve(root.left)
# If height of right subtree is more
elif (right > left):
solve(root.right)
else:
ans = root
return
root = TreeNode(1)
root.left = TreeNode(2)
root.right = TreeNode(3)
ans = None
solve(root)
print(ans.val)
Output
1
People are also reading:
- Find K-th Smallest Element in BST
- Count subarrays with given XOR
- Longest Substring without repeating characters
- Python Take list as an input from a user
- Find MSB in O(1)
- Nth root of M
- Print all subarrays of an array having distinct elements
- Count Inversions
- Hybrid QuickSort Algorithm
- In-place vs out-of-place algorithms




