How to create file in Linux? [Different ways]
1. Using cat command
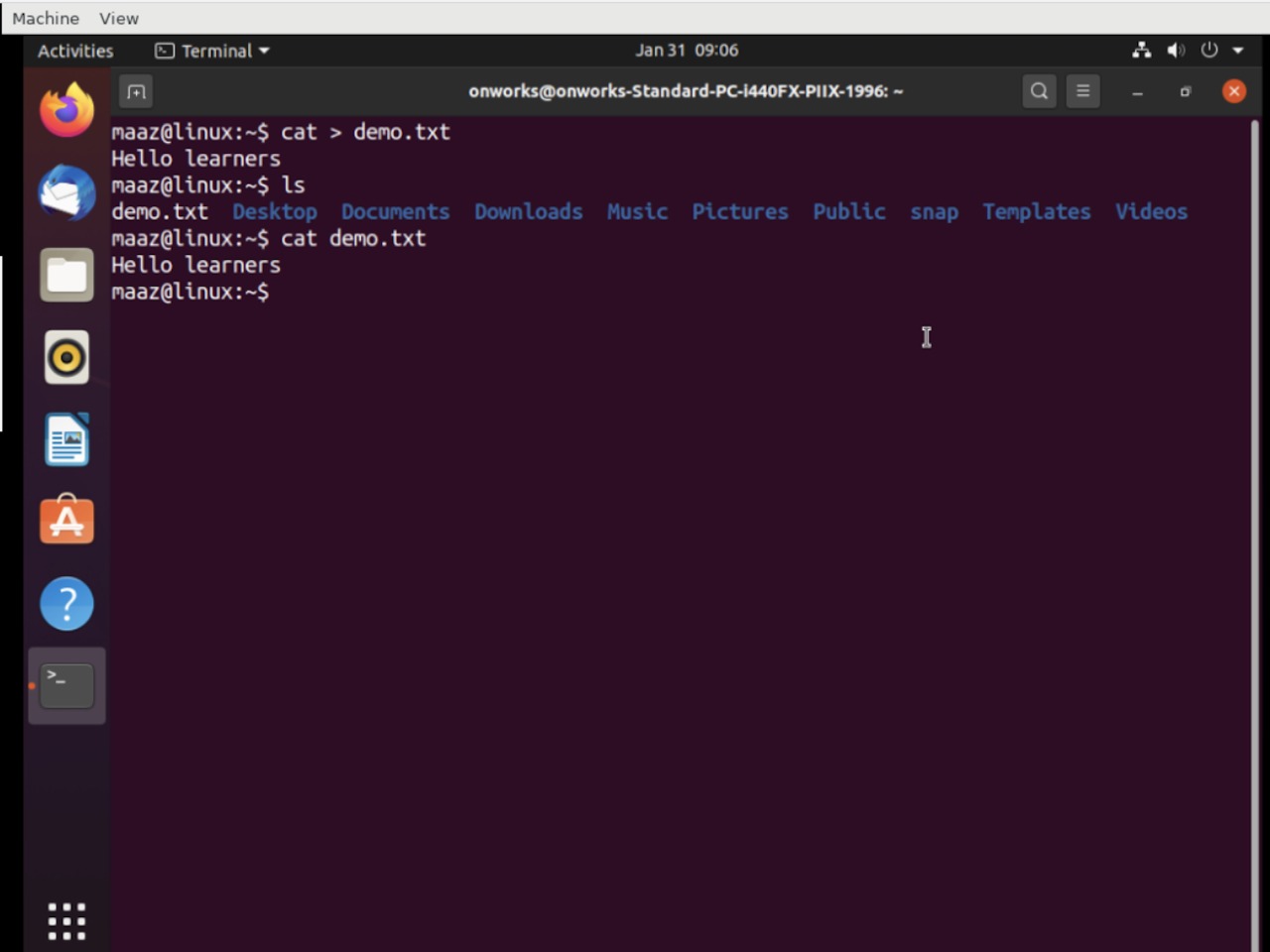
This is a commonly used command in UNIX-like systems which helps us to create, edit, concatenate and view the files. To create a new file using cat command, use the below command:
$ cat > demo.txt
Once you run the above command, the terminal will ask you to write the content that needs to be appended to this file. You can then press ctrl+D to save and exit. If the file with the same name already exists, the content will be overwritten. You can then view the contents of the newly created file using the following command:
$ cat demo.text
2. Using touch command
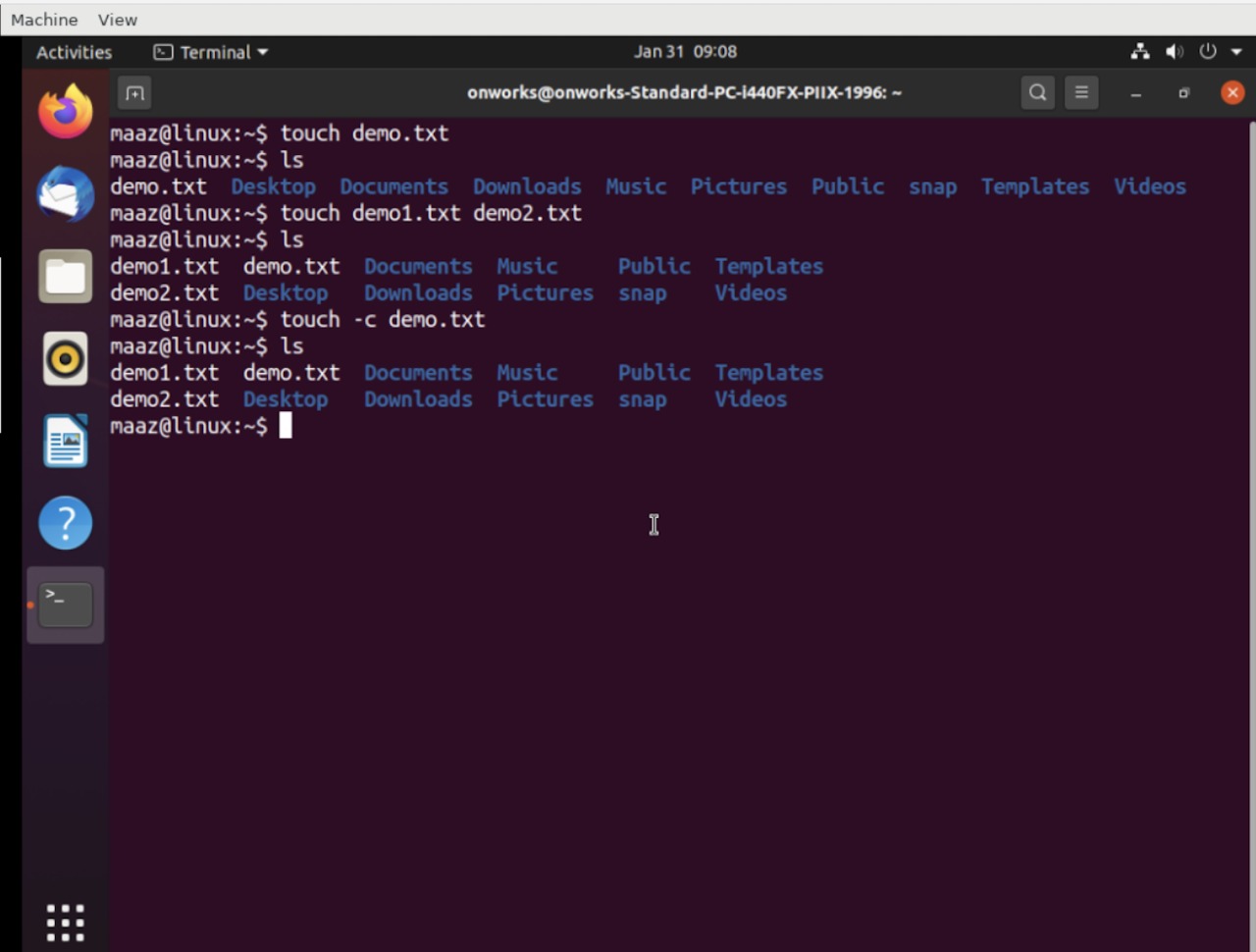
We can use touch commands to create an empty file. Below is the demonstration to create an empty file:
$ touch demo.txt
You can also create multiple files by separating the names of the files using spaces as shown below:
$ touch demo1.txt demo2.txt
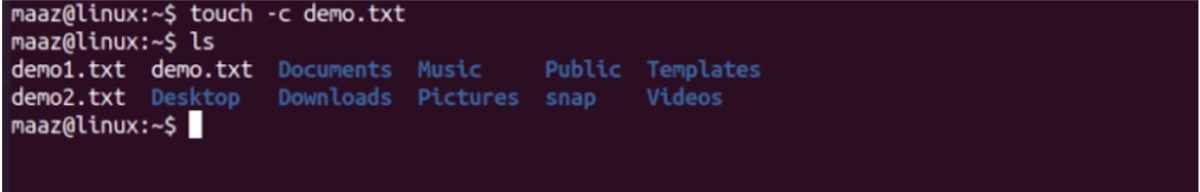
Using -c option with the command checks if the file is already present. In that case, it won't create it again.
$ touch -c demo.txt
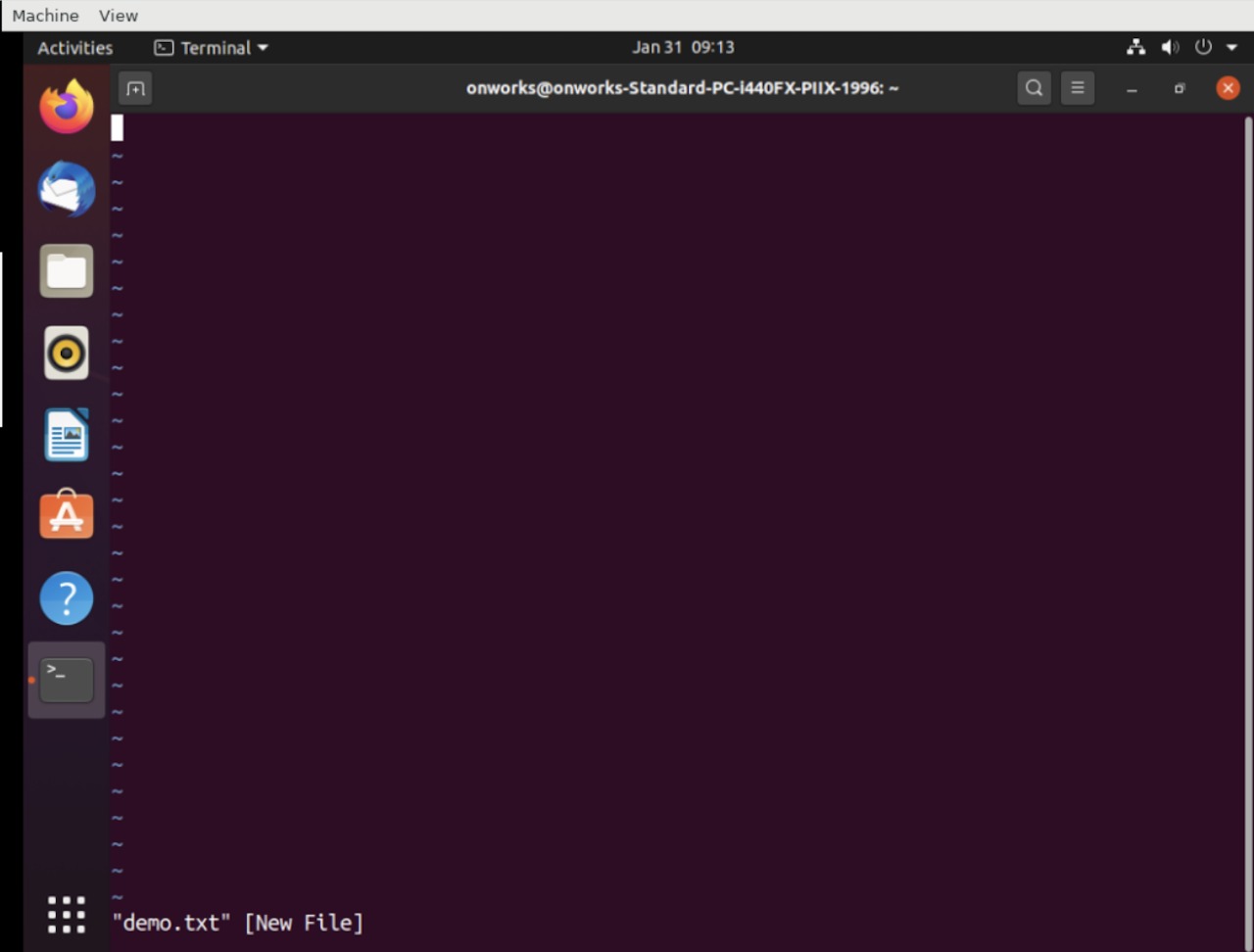
3. Using vi command
This command is primarily built to edit textual content to the files using vi editor. However, if the file you specified with the command does not exist, then it will create a new file with the name and then open it with the text editor.
$ vi demo.txt
Running the above command will open the following editor where you can edit your content in the file.
4. Using echo command
This command displays the specified standard text output in the terminal. However, if you use the redirection operator after the text, this command will create a new file with the content.
$ echo “Hello Learner” > demo.txt
To simply create an empty file, do not specify any content.
$ echo demo.txt
5. Using fallocate command
This command is mostly used to create big files for testing and debugging purposes. The below command will create a new file of size 2 GB.
$ fallocate -l 2G demo.test




