This post details some of the most frequently asked business analyst interview questions. Business analysts have become an important part of any organization, as they help increase business value and also provide cost-effective solutions to businesses.
Generally, the role of a business analyst includes conducting market research, examining various processes, and gauging the overall profitability of the business. They must possess strong interpersonal and data analytics skills so that they can cater to the needs of marketers and managers to make better business decisions.
Though the job profile may vary from business to business, there are several questions that you are likely to encounter in an interview for the business analyst role. The more well-versed you are with what you may hear, the better your chances of acing the interview.
So, whether you are a fresher looking for your first job as a business analyst or a professional planning to take a step further in your career, becoming familiar with the most common (and sometimes tricky) business analyst interview questions can help you win over other candidates.
Business Analyst Interview Questions and Answers
Beginner-level Business Analyst Interview Questions
1. What is business analysis?
Business analysis is a research discipline that helps identify business needs and solutions to businesses. These solutions may include improvements in the process, the development of software or the system components, organizational changes, policy development, and strategic planning.
In simpler terms, business analysis is used to identify different solutions to cater to the needs of businesses. It offers insights into the concepts to be used in developing the initial framework of a project.
Business analysis methods may help you:
- Understand the structure and the other metrics of the company.
- Gauge the problems in the targeted company.
- Identify and accumulate the changes.
- Identify the improvements and recommend solutions to allow organizations to achieve goals.
- Maximize value delivered by the organizations.
2. What is the role of a business analyst? (What can a business analyst do?)
This question will test whether or not you are familiar with your job. Start by explaining that a business analyst's job is to adhere to the business objectives and fulfill the need of stakeholders. Besides, business analysis helps teams design, plan, and validate the developed components.
Here are some key skills business analysis aspirants should have:
- Commercial understanding of different businesses.
- Decision-making and problem-solving skills.
- Expertise in time management.
- Expertise in interpersonal and communication skills.
- Awareness of the project management methodologies.
- The capability to adopt new technologies and software.
3. Why are you fit for the role of a business analyst?
In this question, the interviewer wants to assess whether you meet the company's expectations. Answer this question smartly by putting stress on your education and work experience related to the job. Also, highlight your professional experience and skills that make you fit for the role.
4. Which documents will you handle as a business analyst?
- Project vision document
- Use cases
- User manual
- Requirements management plan
- SRS (System Requirement Specifications)
- BRD ( Business Requirement Documents)
- Test Case Documents
- Functional requirement specifications (FRS)
5. Is there any difference between a data analyst and a business analyst?
A data analyst is an expert in analyzing data and has problem-solving abilities. Moreover, she has a solid knowledge of data statistics, SQL, and data mining. Data analysts perform operations management in an organization. A business analyst, on the other hand, possesses data visualization and decision-making skills. Also, she is an expert in business intelligence, data warehousing, and analytics.
6. Can you list some of the skills and tools used by the business analyst?
- Technical skills and tools: Google Docs, database knowledge, ERP systems, SQL, and MS Office .
- Non-Technical/business analysis skills: Business process management, documentation, and requirement elicitation.
7. How will you (as a business analyst) ensure to gather all the requirements?
As a business analyst, all the requirements are gathered only when:
- Business users authenticate them.
- Requirements are correctly associated with the project.
- Stakeholders are aligned with the complete requirements.
8. Can you list some of the issues that business analysts may encounter?
This is a tricky question, so act smartly and answer. Although issues are part of the work, some of the common ones that you should know about are:
- Not getting access to a particular document.
- Technical issues.
- Business model errors.
9. How do you stay updated with the latest market trends?
With this question, the recruiter wants to know if you follow someone and you are updated with the latest trends and developments. They may gauge you with what actions you take to brush up on your skills and to keep your knowledge up-to-date. You can answer this by referring to some news or publications or may list some webinars and conferences that you have attended.
10. In your past experiences, what documents have you created?
Share some of the documents that you have created. For example, you can say - I have worked on the technical specifications documents, business requirements documents, functional specification documents, use case diagrams, and so on.
11. Can you explain UML and its use cases?
UML stands for Unified Modeling Language, and it is an industry-standard for constructing, visualizing, and documenting various components of a system. While its prime use is for software development, it is also used for organizational functions, business processes, and describing various job roles.
12. What is INVEST?
INVEST is an acronym for Independent, Negotiable, Valuable, Estimable, Sized appropriately, and Testable. Business analysts use this to ensure the delivery of quality services and products.
- Independent: This means every user story should be different and self-contained to avoid any dependencies on the other users’ stories.
- Negotiable : A story should be short and not detailed; because it will help encourage the ongoing conversation. Moreover, it will provide scope for the negotiation between the customer and the developers.
- Valuable: The story should provide valuable insights; if the customers cannot think of a value statement, you may eliminate it. Another reason for having a value statement is that value indicates why we are building specific features.
- Estimable: Developers need to estimate every story; the key factors of estimation are properly sized stories, technical knowledge as well as domain knowledge.
- Testable: This helps determine the completeness; a story should have some acceptance criteria and can be measured and tested.
13. What is SRS, and what are its key elements?
A System Requirements Specifications (SRS) is a document or a set of documents that describe the features of a software application. It includes various elements that define the functionality required by the stakeholders and customers. The key elements of SRS are:
- Scope of Work
- Functional Requirements
- Data Model
- Acceptance Criteria
- Dependencies
- Non-functional Requirements
- Acceptance Criteria
14. What steps will you follow to create a product when you only have an idea?
With this question, recruiters want to know your workflow or the process you follow with your projects. Your answer can be like this; I usually first perform market analysis, followed by competitor analysis, and so on. Alternatively, you can also give a detailed answer by mentioning the following steps:
- Market analysis
- Competitor analysis
- SWOT analysis
- Personas
- Strategic vision
- Future set
- Use cases
- SDLC
- Test cases
- Monitoring
- Scalability
15. What is a BRD? Are BRD and SRS the same?
BRD means Business Requirement Document. It is a formal contract between the organization and the customer. No, BRD and SRS are not the same. The business analyst creates BRD, whereas SRS is based on the needs of technical experts.
16. What do you know about the term ‘Requirement’ in business analysis?
A requirement in business analysis is a targeted solution, which helps in defining business-specific goals and objectives. It is like an input to the different stages of SDLC .
17. Is the Requirement good?
Yes, a good requirement is Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Timely (SMART). The description should be perfect, and all other requirements parameters should be attainable.
18. What is a use case?
A use case is a diagrammatic representation of the system that defines how customers will use the software or system to accomplish a goal. It is one of the most important parts of the software modeling technique, and it defines the resolution of any errors which customers may encounter.
19. Are there any particular steps you need to follow when designing a use case?
Yes, you need to follow these steps:
- Identify the user of the system.
- Make a new user profile for every category of users. This may include all the roles that users may play.
- Identify goals.
- Create use cases for every goal associated with the use case template. This may include maintaining the same abstraction level for every use case.
- Structure use cases.
- Review and validate users.
20. What is gap analysis?
Gap analysis is a simple technique that helps to analyze the performance gap between the existing system and the target system. Here the gap defines the changes that the system needs to deliver the expected results. A gap is also a performance level comparison between the current and the proposed functionalities.
Intermediate-level Business Analyst Interview Questions
21. What is CATWOE? How does it help business analysts?
CATWOE means Customers, Actors, Transformation process, Worldview, Owners, and Environmental constraints. CATWOE is all about gauging decisions and how these decisions affect the customer, the unique transformations, and so on.
22. Have you heard about Waterfall and Spiral models? Which, according to you, is better?
A :
Waterfall Model: The waterfall model is sequential; this means that before you initiate one stage/phase, the previous stage/phase has to be completed. The main stages of the Waterfall model are as follows:
- Planning
- Initiation
- Analysis
- Design construction
- Testing
- Implementation
- Maintenance
Spiral Model : The spiral model is a combination of waterfall and iterative models. It combines the iterative development process model with the waterfall model. You should use the spiral model when:
- Releases are very frequent.
- The creation of a prototype is applicable.
- Risk and cost evaluation is important.
- Changes are required at any time.
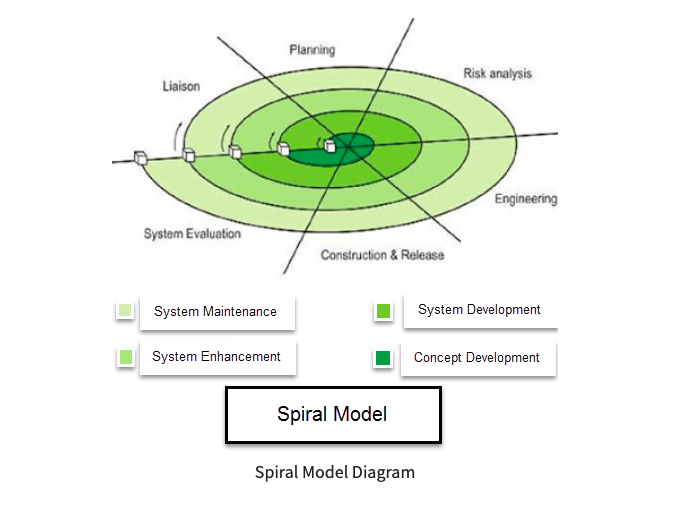
The type of model that you should use depends upon the scope of the project and the company's culture.
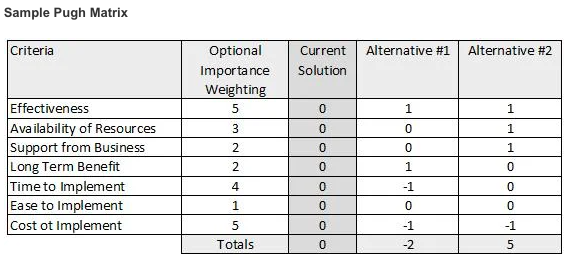
23. What is Pugh Matrix?
Pugh Matrix defines the optimal and alternate solutions. It is the standard part of the Six Sigma technique and is also known as a problem or the design matrix. It allows business consultants and analysts to organize various features or criteria of a solution in a structured way for making comparisons.
With this matrix, analysts can develop a solution, which is a hybrid, for concept generation and selection. Also, the Pugh matrix is known by various names like:
- Selection Matrix
- Decision Matrix
- Problem Matric
- Opportunity analysis
- Criteria rating form
- Criteria-based matrix
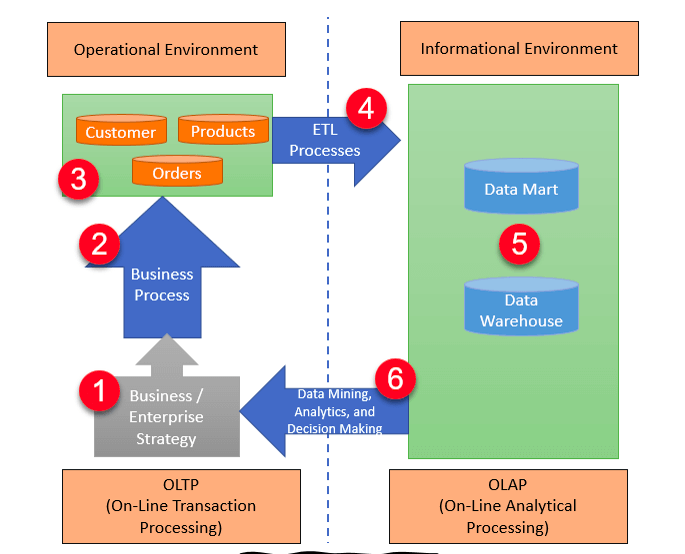
24. What is the full form Of OLTP?
OLTP means Online Transaction Processing; this system can do all the database transactions and is used for data entry and retrieving. OLTP is basically focused on maintaining data integrity and query processing in multi-access environments.
The following are some characteristics of OLTP:
- It uses transactions that include a small amount of data.
- It has various users.
- Indexed data can be accessed easily.
- It uses a fully normalized schema for consistency.
- It has a short response time.
The Architecture of OLTP:
25. What is 8-Omega? 8-Omega is a business framework that organizations and firms use to improve their business. The key pointers of 8-omega are strategy, people, process, and technology. Primarily, the 8-Omega framework has 8 different stages through which each perspective goes through:
- Discover: Identification of current and future business strategy.
- Analyze: Analysis of ongoing processes.
- Design: New process configurations.
- Integrate: Integration with the existing system.
- Implement: Implementation of new processes.
- Manage: Management of new solutions.
- Control: Continuous review and monitoring of the new process.
- Improve: Performance review and adjustments based on requirements.
26. How do you define an Agile Business Analyst? What are its core qualities?
As an agile business analyst, you must be able to:
- Perform requirement development effectively.
- Collaborate with the stakeholders and product owners to get the product requirements.
- Understand all the responsibilities of an agile business analyst, along with agile terminologies.
27. What is the Waterfall Model?
The Waterfall Model is a structured software development methodology that does not need any direct customer involvement. It is a sequential design process and is difficult to execute (as compared to the agile model).
28. What is the BPMN Gateway?
BPMN Gateway is primarily used for monitoring the flow of interaction and the classification of processes. Some of the elements of the BPMN Gateway are:
- Flow objects
- Data connection objects
- Swimlanes
- Artifacts
29. What is Pareto Analysis?
Pareto Analysis is a decision-making technique called the 80/20 rule that is used for quality control. The Pareto Principle explains that 80% of the problems are due to 20% of the causes. It also states that 80% results of a project depend on 20% of the overall work or efforts.
To comprehend the phenomenon, take an example of a restaurant, where 80% of the problems are generated by 20% of the factors that are used in running the business. All you have to do is track that 20% of factors are responsible for 80% of issues and work on them to boost the ROI of the business.
30. Define Kano Analysis.
The Kano Model can be a helpful framework for product teams who have limited resources and time but wants to ensure that they prioritize the appropriate customer behavior. It is one of the many prioritization frameworks that are made for product teams to help them prioritize initiatives.
For instance, Kano can assist with the identification of features that can satisfy a particular need of customers. By using this model, the product team can list all the new features required for constructing the product roadmap. The product team will then need to figure out two important aspects of each feature:
- Potential to satisfy each customer.
- Investment is required to implement the feature.
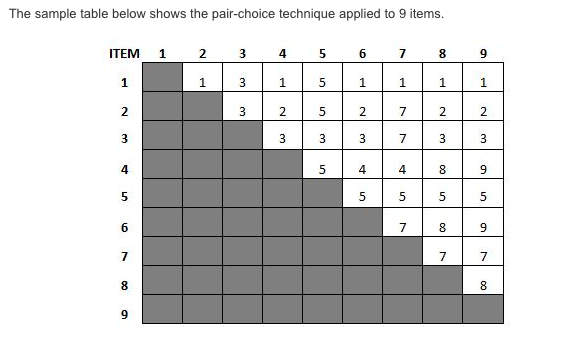
31. What do you know about the Pair-Choice Technique?
The Pair-Choice Technique is used to prioritize the various items involved in the process of business analysis. This technique is mainly used when different stakeholders are involved in a project.? The Pair-Choice Technique asks every customer to compare each item against another item.
32. Have you ever heard about the Kanban tool?
Kanban is a project management tool that helps agile teams to manage work visually. This tool also works as a scheduling system and is used to describe the current development status of projects.
Kanban board uses Swimlanes, WIP Limits, Cards, and Columns to let teams visualize and manage workflows effectively. Following are the main components of the Kanban Board:
- Kanban Cards: This is the visual representation of tasks where each card contains information about the task and its deadlines.
- Columns: Every column on the Kanban board represents a different stage of the workflow. The cards move through the columns (stages) until they are completed.
- Work-in-Progress Limits: These limits restrict the number of tasks at different stages of the workflow.
- Swimlanes : These are horizontal lanes that you can use to separate different teams, activities, services, and more.
- Commitment Point: A commitment is a point when you can pull off an item in the system when the work process is completed.
- Delivery Point : It’s a point in the workflow where the work items are considered to be finished.
33. What is Scope Creep?
Scope Creep is the uncontrolled or abrupt variations in the scope of a project that occur without making any changes to the project's resources. This occurs because of miscommunication.
34. What is RUP?
Rational Unified Process (RUP) is a software development process for an object-oriented model that assures top-notch software production and project management. RUP divides the project life cycle into four different phases, with each phase focusing on the core disciplines like analysis, design, modeling, and implementation in a business model.
These four phases are:
- Inception : At this phase, the idea of the project is stated; the development team identifies if the project is worth working on and what resources are required for it.
- Elaboration : The project’s architecture and required resources are then evaluated.
- Construction : At this stage, the software system is created, and the project is developed and created.
- Transition : The software is then released to the public after final adjustments and updates.
35. What is RAD methodology?
RAD is a part of the agile software development methodology to keep pace with the needs of businesses and clients. RAD comprises these five phases:
- Define and Finalize the Project Requirements: At this step, the stakeholders sit together to identify the project requirements like project goals, expectations, budget, and deliverables.
- Building Prototype: This step includes a development process, which means the developers and designers work together to finalize the product.
- Gathering Feedback: At this stage, the prototypes and beta systems are then converted into working models and are tested from the user's perspective. The user feedback is gathered, and respective changes are made to create the best product.
- Test: This includes testing the software to ensure that the project is built as per the client’s requirements.
- Presentation: The presentation includes data conversions, user training, and more testing to ensure that everything runs smoothly before the product goes to launch.
36. Can we use the Waterfall Model in place of Scrum?
Yes, only when the requirements are simple and easily understandable.
37. What is a feasibility study?
A feasibility study, as the name suggests, helps to assess whether a project or plan is feasible. It is an assessment method that shows the practicality of a project/plan. It is conducted to objectively uncover the strengths, weaknesses, and threats to ascertain the likelihood of completing any project successfully. A company may conduct a feasibility study before launching a new project or business.

38. What is the difference between iterative development and incremental development?
Iterative software development occurs without any interruption. In this, the software development cycle is repeated till the final product comes out. On the other hand, in the incremental model, the software development model is not repeated; rather, it passes through three steps, viz. design, execution, and testing, till the project is completed.
39. What are pool and swimlane?
A pool is a dedicated activity for a single person, while a swimlane is related to a group of activities performed on an activity diagram .
40. Can you differentiate between the Fish Model and the V Model?
The fish model is used when there are no specific requirements from the customer's side. Otherwise, the V-model becomes an ideal choice.
- The fish model includes continuous and simultaneous deployment of verification and validation processes.
- V-model is a software development model that is designed to understand the complexity associated with the system under development.
Advanced-level Business Analyst Interview Questions
41. How will you handle the ever-changing needs of customers while developing any system?
As a business analyst, I will first get clear instructions about the needs and requirements and then have a self-attested document saying that no changes will be made after a certain period.
42. What is PEST?
PEST means Political, Economic, Social, and Technological; it is used to analyze the business environment. In other terms, it is a management method where an organization can assess all the external factors that influence its operation so as to become competitive in the market. Generally, PEST is more effective with big organizations and is often used with the SWOT analysis.
43. What is SWEBOK?
SWEBOK stands for Software Engineering Body of Knowledge. It defines the sum of knowledge gathered within the literature, which describes the profession of software engineering.
44. What is JAD?
JAD stands for Joint Application Development. It is a method where the client and the end-user come together for the design and development of a project. It consists of approaches that help in approving the quality of specifications and user participation through JAD sessions.
45. What is ETL?
ETL means Extraction, Transformation, and Load; it is a data processing method typically used in data warehousing to replicate the data from one source to another targeted system. Here are the steps of ETL:
- Extraction : This is the first step that involves copying data from one source.
- Loading : In this step, the pipeline data is replicated.
- Transformation : Once the data gets into the targeted system, organizations can make whatever transformations they need.
46. What are the different types of diagrams you encounter in business analysis?
- Flowcharts : These help in illustrating all the technical and non-technical operations.
- Activity Diagrams : This type of diagram illustrates different activities and their flow in various departments.
- Use Case Diagrams : These diagrams define the functionality of a system by using a set of actions, functions, and services.
- Sequence Diagrams : These diagrams help illustrate the interaction between objects and the time sequence of the message flow.
47. What is Black Box Testing?
Black box testing is a kind of testing when the complete software unit (instead of sub-parts) is tested without considering its contents or source code. It tests the system against all the external factors that are responsible for software failure. This testing focuses on the inputs and outputs produced by a software product. Various parameters that are checked in black box testing are:
- System’s interaction with the inputs
- Response time of the system
- Usability issues
- Performance issues
48. What is CaaS?
CaaS means Communication-as-a-Service. It is outsourced from the schema interaction and can be leased.
49. What is OOAD?
OOAD is Object-oriented analysis and designing; it is used for languages like C++ and Java.
50. What is UAT?
The full form of UAT is User acceptance testing; if the UAR fails, it is a type of testing performed by end-users to verify the system before moving to software development. The main purpose of this testing is to validate the end-to-end business flow.
51. Why should you use a Sprint Burndown Chart?
A sprint burndown chart depicts the rate of progress of the current spring. This is regularly updated with time.
52. Explain the Velocity of a Sprint?
The velocity of a Sprint is the total work done by the development team during the Sprint. The Sprint velocity depends upon the historical data available in the previous Sprint of the project.
53. What are the documents that a business analyst may encounter?
Some of the documents that you need to work with as a business analyst are:
- Project scope.
- Fact sheet for the constraints.
- Functional documents like UML, Activity, Dataflow diagrams, and so on.
- Testing phase documents like a plan, QA testing, and tests.
Conclusion
Every company wants to hire a business analyst who has excellent knowledge. Hence, to be a pro as a business analyst, you must be good at collecting and analyzing data to streamline various business processes.
While you are appearing for a business analyst interview, you need to make sure that you showcase your skills and present an impactful resume. Also, you can brush up your skills with the business analyst interview questions and answers mentioned above.
P.S. : If you have been to any business analyst interview and want to share some important questions, comment below and help your fellow mates!
People are also reading:





Leave a Comment on this Post