As per the summary of configuration management (CM), it is a system engineering process to establish and maintain uniformity of the product's performance, physical and functional attributes by its design, operational information, and requirements during its life. The configuration management (CM) process is broadly used in military engineering organizations to manage changes during the system life cycle of the complex system, like military vehicles, weapon systems, and information systems.
Besides the military, the CM process is used in IT service management as described by ITIL and other domain models in civil engineering or other industrial engineering divisions like bridges, dams, roads, canals, and buildings.
What is Configuration Management? [Definition]
It is the method to assure that any software and hardware assets that the company owns are identified and followed at all times for every future change to these assets are identified and followed. You can consider configuration management, such as an always up-to-date inventory for your technology assets and the single source of truth.
Configuration management usually crosses a few areas. It usually relates to many ideas, such as creating “software pipelines” for building and testing software artifacts. It might relate to writing “infrastructure-as-code” for capturing in code a current state of infrastructure. It could mean incorporating configuration management tools like Chef, Ansible, and Puppet for storing the current state of servers.
Configuration management refers to the variety of systems, but you will be involved with these:
- Servers
- Applications
- Operating systems
- Databases and other storage systems
- Networking
- Software
Process steps of the configuration management
The configuration management process consists of five key steps for projecting configuration management:
- Planning: The configuration management plan describes how you can track, record, audit configuration, and control. These documents are usually part of a project quality management plan.
- Identification: Any configuration specifications on the project must be classified and registered, including design requirements, functionality requirements, and every other specification. The finish of this method results in a configuration baseline for a project.
- Control: As a project scope is modified, the impact on a configuration should be evaluated, documented, and approved. This is usually done in a project change control process.
- State accounting: Track the project configuration at all times. You must be capable of informing the version the configuration is on and have a historical record of old versions. It is essential to have an account of all versions so you can follow changes during the project.
- Audit: It includes any tests for proving that a product complies with configuration requirements. Assume you created the report that needs to run in 10 seconds. Audit tests to see if the completed report actually runs that fast. Usually, audits and checks will be built in after significant project phases.
Benefits of Configuration Management
There are various benefits of a configuration management system, and they are:
1. Organization
Being that Configuration Management resembles the framework for more prominent information management programs, it ought to abandon saying that it is necessary for more prominent management and organization of information overall. With an all-around ordered system set up, a decent IT worker ought to have the option to see the entirety of the past system usage of the business, and can all the more likely location future needs and changes to stay up with the latest and running efficiently.
2. Reliability
Nothing is more regrettable than a temperamental system that is continually down and requiring fixes because an organization's configuration management group is inadequate in an organization and expert liveliness. If the system is utilized accurately, it should run like the all-around oiled machine that it is, guaranteeing that each division in the organization can complete its employment appropriately.
Expanded solidness and proficiency of the system will stream down into each division of an organization, including client relations, as the simplicity and speed wherein their issues can be explained and information can be gotten to will definitely have a constructive outcome.
3. Cost Reduction and Risks
Like whatever else in business, an absence of support and consideration regarding subtleties can have more severe dangers and cost down the line instead of proactive activity before an issue emerges. Configuration Management sets aside cash with steady system upkeep, record keeping, and governing rules to forestall redundancy and missteps.
The composed record keeping of the system itself spares time for the IT office and decreases squandered cash for the organization, with less cash being spent on fixing repeating or counter-intuitive issues. With a refreshed system, there is likewise a decrease in the dangers of expected claims for breaks of security because of the obsolete programming framework, which might be ascribed to carelessness. With the usage of this system, there is actually nothing to lose. However, everything for obtaining.
Software for Configuration Management
The software configuration management (SCM) method is viewed by practitioners as the most reliable solution for managing changes in the software project. This identifies the physical and functional attributes of the software at different points in time and works systematically to control the change to identify attributes for maintaining software integrity as well as traceability during the software development life cycle.
The process of SCM further defines the need to trace changes and the facility for verifying that the decisive delivered software has all of the planned improvements that are deemed to be involved in a release. It recognizes four procedures that must be defined for each software project to ensure that the sound SCM process is completed. They are:
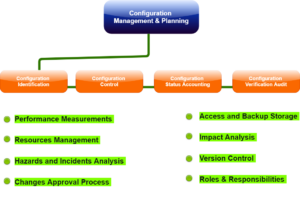
- Configuration identification
- Configuration control
- Configuration status accounting
- Configuration audits
These definitions and terms vary from standard to standard but are necessarily the same.
- Configuration identification: It is a process for identifying the attributes that define all aspects of the configuration item. The configuration item is a product that has an end-user way. These particular attributes are registered in the configuration documentation and baselined. The baseline is an attribute force formal configuration that varies control processes to get affected in case these attributes are modified.
- Configuration change control: It is a set of approval stages and processes required for changing the configuration item attributes and re-baseline them.
- Configuration status accounting: It is the ability to record and report on configuration baselines associated with all configuration items at any moment.
- Configuration audit: It breaks into functional and physical configuration audits, and they occur either on delivery or at the moment of effecting the variation. The functional configuration audit assures that performance and functional attributes of the configuration item are completed, in a physical configuration audit assures that the configuration item is installed by the requirements of the detailed design documentation.
Conclusion
As we have already disused, configuration management (CM) is a system engineering process to establish and maintain uniformity of the product's performance and physical and functional attributes by its design, operational information, and requirements during its life. In this article, we have provided complete information regarding configuration management (CM).
People are also reading:
- How to Uninstall Chromium?
- Software Developer Salary
- What does a Software Developer Do?
- Desktop Applications vs Web Applications
- How to Allocate More RAM to Minecraft?
- How to Become a Software Developer?
- Best Animation Software
- Composition Analysis vs Static Application Security Testing
- Best Remote Desktop Software
- Best Open Source Monitoring Software




Leave a Comment on this Post